Classifying oxidative stress by F2-isoprostane levels across human diseases: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 28391180
- PMCID: PMC5384299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.03.024
Classifying oxidative stress by F2-isoprostane levels across human diseases: A meta-analysis
Abstract
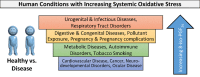
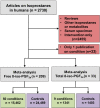
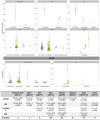
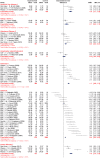
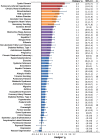
The notion that oxidative stress plays a role in virtually every human disease and environmental exposure has become ingrained in everyday knowledge. However, mounting evidence regarding the lack of specificity of biomarkers traditionally used as indicators of oxidative stress in human disease and exposures now necessitates re-evaluation. To prioritize these re-evaluations, published literature was comprehensively analyzed in a meta-analysis to quantitatively classify the levels of systemic oxidative damage across human disease and in response to environmental exposures. In this meta-analysis, the F2-isoprostane, 8-iso-PGF2α, was specifically chosen as the representative marker of oxidative damage. To combine published values across measurement methods and specimens, the standardized mean differences (Hedges' g) in 8-iso-PGF2α levels between affected and control populations were calculated. The meta-analysis resulted in a classification of oxidative damage levels as measured by 8-iso-PGF2α across 50 human health outcomes and exposures from 242 distinct publications. Relatively small increases in 8-iso-PGF2α levels (g<0.8) were found in the following conditions: hypertension (g=0.4), metabolic syndrome (g=0.5), asthma (g=0.4), and tobacco smoking (g=0.7). In contrast, large increases in 8-iso-PGF2α levels were observed in pathologies of the kidney, e.g., chronic renal insufficiency (g=1.9), obstructive sleep apnoea (g=1.1), and pre-eclampsia (g=1.1), as well as respiratory tract disorders, e.g., cystic fibrosis (g=2.3). In conclusion, we have established a quantitative classification for the level of 8-iso-PGF2α generation in different human pathologies and exposures based on a comprehensive meta-analysis of published data. This analysis provides knowledge on the true involvement of oxidative damage across human health outcomes as well as utilizes past research to prioritize those conditions requiring further scrutiny on the mechanisms of biomarker generation.
Keywords: F(2)-isoprostane; Meta-analysis; Oxidative damage; Oxidative stress; Ranking.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures






Comment in
-
Classifying oxidative stress by F2-Isoprostane levels in human disease: The re-imagining of a biomarker.Redox Biol. 2017 Aug;12:897-898. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.028. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28467952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van't Erve T.J., Lih F.B., Jelsema C., Deterding L.J., Eling T.E., Mason R.P., Kadiiska M.B. Reinterpreting the best biomarker of oxidative stress: the 8-iso-prostaglandin F2a/prostaglandin F2a ratio shows complex origins of lipid peroxidation biomarkers in animal models. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2016;95:65–73. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kadiiska M.B., Gladen B.C., Baird D.D., Dikalova A.E., Sohal R.S., Hatch G.E., Jones D.P., Mason R.P., Barrett J.C. Biomarkers of oxidative stress study: are plasma antioxidants markers of CCl(4) poisoning? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000;28:838–845. - PubMed
-
- Kadiiska M.B., Gladen B.C., Baird D.D., Germolec D., Graham L.B., Parker C.E., Nyska A., Wachsman J.T., Ames B.N., Basu S., Brot N., Fitzgerald G.A., Floyd R.A., George M., Heinecke J.W., Hatch G.E., Hensley K., Lawson J.A., Marnett L.J., Morrow J.D., Murray D.M., Plastaras J., Roberts L.J., II, Rokach J., Shigenaga M.K., Sohal R.S., Sun J., Tice R.R., Van Thiel D.H., Wellner D., Walter P.B., Tomer K.B., Mason R.P., Barrett J.C. Biomarkers of oxidative stress study II. Are oxidation products of lipids, proteins, and DNA markers of CCl4 poisoning? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005;38:698–710. - PubMed
-
- Kadiiska M.B., Gladen B.C., Baird D.D., Graham L.B., Parker C.E., Ames B.N., Basu S., Fitzgerald G.A., Lawson J.A., Marnett L.J., Morrow J.D., Murray D.M., Plastaras J., Roberts L.J., II, Rokach J., Shigenaga M.K., Sun J., Walter P.B., Tomer K.B., Barrett J.C., Mason R.P. Biomarkers of oxidative stress study III. Effects of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents indomethacin and meclofenamic acid on measurements of oxidative products of lipids in CCl4 poisoning. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005;38:711–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

