Accurate Classification of Protein Subcellular Localization from High-Throughput Microscopy Images Using Deep Learning
- PMID: 28391243
- PMCID: PMC5427497
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.116.033654
Accurate Classification of Protein Subcellular Localization from High-Throughput Microscopy Images Using Deep Learning
Abstract
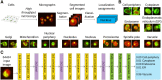
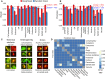
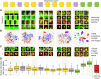
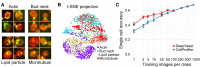
High-throughput microscopy of many single cells generates high-dimensional data that are far from straightforward to analyze. One important problem is automatically detecting the cellular compartment where a fluorescently-tagged protein resides, a task relatively simple for an experienced human, but difficult to automate on a computer. Here, we train an 11-layer neural network on data from mapping thousands of yeast proteins, achieving per cell localization classification accuracy of 91%, and per protein accuracy of 99% on held-out images. We confirm that low-level network features correspond to basic image characteristics, while deeper layers separate localization classes. Using this network as a feature calculator, we train standard classifiers that assign proteins to previously unseen compartments after observing only a small number of training examples. Our results are the most accurate subcellular localization classifications to date, and demonstrate the usefulness of deep learning for high-throughput microscopy.
Keywords: deep learning; high-content screening; machine learning; microscopy; yeast.
Copyright © 2017 Parnamaa and Parts.
Figures
References
-
- Alipanahi B., Delong A., Weirauch M. T., Frey B. J., 2015. Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA- and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 33: 831–838. - PubMed
-
- Boland M. V., Murphy R. F., 2001. A neural network classifier capable of recognizing the patterns of all major subcellular structures in fluorescence microscope images of HeLa cells. Bioinformatics 17(12): 1213–1223. - PubMed
-
- Boland M. V., Markey M. K., Murphy R. F., 1998. Automated recognition of patterns characteristic of subcellular structures in fluorescence microscopy images. Cytometry 33(3): 366–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
