Increased brain expression of GPNMB is associated with genome wide significant risk for Parkinson's disease on chromosome 7p15.3
- PMID: 28391543
- PMCID: PMC5522530
- DOI: 10.1007/s10048-017-0514-8
Increased brain expression of GPNMB is associated with genome wide significant risk for Parkinson's disease on chromosome 7p15.3
Abstract
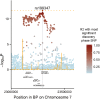
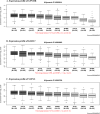
Genome wide association studies (GWAS) for Parkinson's disease (PD) have previously revealed a significant association with a locus on chromosome 7p15.3, initially designated as the glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) locus. In this study, the functional consequences of this association on expression were explored in depth by integrating different expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) datasets (Braineac, CAGEseq, GTEx, and Phenotype-Genotype Integrator (PheGenI)). Top risk SNP rs199347 eQTLs demonstrated increased expressions of GPNMB, KLHL7, and NUPL2 with the major allele (AA) in brain, with most significant eQTLs in cortical regions, followed by putamen. In addition, decreased expression of the antisense RNA KLHL7-AS1 was observed in GTEx. Furthermore, rs199347 is an eQTL with long non-coding RNA (AC005082.12) in human tissues other than brain. Interestingly, transcript-specific eQTLs in immune-related tissues (spleen and lymphoblastoid cells) for NUPL2 and KLHL7-AS1 were observed, which suggests a complex functional role of this eQTL in specific tissues, cell types at specific time points. Significantly increased expression of GPNMB linked to rs199347 was consistent across all datasets, and taken in combination with the risk SNP being located within the GPNMB gene, these results suggest that increased expression of GPNMB is the causative link explaining the association of this locus with PD. However, other transcript eQTLs and subsequent functional roles cannot be excluded. This highlights the importance of further investigations to understand the functional interactions between the coding genes, antisense, and non-coding RNA species considering the tissue and cell-type specificity to understand the underlying biological mechanisms in PD.
Keywords: Antisense and non-coding RNA; Chr7 locus (GPNMB); Human brain expression QTLs; Parkinson’s disease (PD); Risk SNP rs199347.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
The Braineac project was supported by the MRC through the MRC Sudden Death Brain Bank Grant (MR/G0901254) to J.H. P.A.L. was supported by the MRC (grants MR/N026004/1 and MR/L010933/1) and Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. D.T. was supported by the King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Saudi Arabia, and the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and MRC grant (MR/N026004/1). M.M. was funded by the DST INSPIRE Fellowship (IF120351), DST India, and the Newton Bhabha Fund by the British Council and DBT India. We acknowledge support from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Figures


References
-
- Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M, DeStefano AL, Kara E, Bras J, Sharma M, Schulte C, Keller MF, Arepalli S, Letson C, Edsall C, Stefansson H, Liu X, Pliner H, Lee JH, Cheng R, International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics C, Parkinson’s Study Group Parkinson’s Research: The Organized GI, andMe, GenePd, NeuroGenetics Research C, Hussman Institute of Human G, Ashkenazi Jewish Dataset I, Cohorts for H, Aging Research in Genetic E, North American Brain Expression C, United Kingdom Brain Expression C, Greek Parkinson’s Disease C, Alzheimer Genetic Analysis G. Ikram MA, Ioannidis JP, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Bis JC, Martinez M, Perlmutter JS, Goate A, Marder K, Fiske B, Sutherland M, Xiromerisiou G, Myers RH, Clark LN, Stefansson K, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Chen H, Wood NW, Houlden H, Payami H, Brice A, Scott WK, Gasser T, Bertram L, Eriksson N, Foroud T, Singleton AB. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 2014;46(9):989–993. doi: 10.1038/ng.3043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trabzuni D, Ryten M, Emmett W, Ramasamy A, Lackner KJ, Zeller T, Walker R, Smith C, Lewis PA, Mamais A, de Silva R, Vandrovcova J, International Parkinson Disease Genomics C. Hernandez D, Nalls MA, Sharma M, Garnier S, Lesage S, Simon-Sanchez J, Gasser T, Heutink P, Brice A, Singleton A, Cai H, Schadt E, Wood NW, Bandopadhyay R, Weale ME, Hardy J, Plagnol V. Fine-mapping, gene expression and splicing analysis of the disease associated LRRK2 locus. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

