Early phase dynamics of traceable mCherry fluorescent protein-carrying HIV-1 infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells-transplanted NOD/SCID/Jak3-/- mice
- PMID: 28392419
- PMCID: PMC7900919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.03.027
Early phase dynamics of traceable mCherry fluorescent protein-carrying HIV-1 infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells-transplanted NOD/SCID/Jak3-/- mice
Abstract
We attempted to elucidate early-phase dynamics of HIV-1 infection using replication-competent, red-fluorescent-protein (mCherry)-labeled HIV-1JR-FL (HIVJR-FLmC) and NOD/SCID/Jak3-/- mice transplanted with Individual-A's human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMC)(hNOJ mice). On day 7 following HIVJR-FLmC inoculation, mCherry-signal-emitting infection foci were readily identified in the subserosa of 10 of 10 HIVJR-FLmC-inoculated hNOJ mice, although infection foci were not located without the mCherry signal in unlabeled HIV-1JR-FL-inoculated mice (n = 6). Even on day 14, infection foci were hardly located in the unlabeled HIV-1JR-FL-inoculated mice, while in all of 7 HIVJR-FLmC-inoculated hNOJ mice examined, mCherry-signal-emitting lymph nodes were easily identified, in which active viral replication was present. On day 14, a significantly larger number of mesenteric lymph nodes were seen in HIVJR-FLmC-exposed hNOJ mice than in HIVJR-FLmC-unexposed mice (P = 0.0025). The weights of mesenteric lymph nodes of those HIVJR-FLmC-exposed hNOJ mice were also greater than those of HIVJR-FLmC-unexposed mice (P = 0.0005). When hNOJ mice were inoculated with HIVJR-FLmC-exposed hPBMC from Individual-B, significantly greater viremia was seen than in cell-free HIVJR-FLmC-inoculated hNOJ mice as examined on day 7. In the lymph nodes of those mice inoculated with HIVJR-FLmC-exposed hPBMC from Individual-B, a substantial number of Individual-B's HIVJR-FLmC-infected cells were identified together with Individual-A's cells as examined on day 14. The present HIVJR-FLmC-infected mouse model represents the first system reported using traceable HIVJR-FLmC and human target cells, not using SIV or simian cells, which should be of utility in studies of early-phases of HIV-1 transmission and in evaluating the effects of potential agents for post-exposure and pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Keywords: Cell-associated HIV infection; Early phase dynamics; HIV propagation; In vivo imaging.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

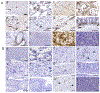
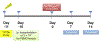

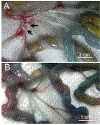


Similar articles
-
Raltegravir blocks the infectivity of red-fluorescent-protein (mCherry)-labeled HIV-1JR-FL in the setting of post-exposure prophylaxis in NOD/SCID/Jak3-/- mice transplanted with human PBMCs.Antiviral Res. 2018 Jan;149:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 28893602 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of activated memory CD4+ T cells affects infectivity of CCR5-tropic HIV-1 in humanized NOD/SCID/JAK3null mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053495. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23301078 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of baboons with simian/human immunodeficiency viruses.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Aug 15;9(5):429-41. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995. PMID: 7627620
-
A Simple Mouse Model for the Study of Human Immunodeficiency Virus.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016 Feb;32(2):194-202. doi: 10.1089/AID.2015.0211. Epub 2015 Dec 17. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016. PMID: 26564392 Free PMC article.
-
SCID-hu mice: a model for studying disseminated HIV infection.Semin Immunol. 1996 Aug;8(4):223-31. doi: 10.1006/smim.1996.0028. Semin Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8883145 Review.
Cited by
-
Raltegravir blocks the infectivity of red-fluorescent-protein (mCherry)-labeled HIV-1JR-FL in the setting of post-exposure prophylaxis in NOD/SCID/Jak3-/- mice transplanted with human PBMCs.Antiviral Res. 2018 Jan;149:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 28893602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asmal M, Lane S, Tian M, Nickel G, Venner C, Dirk B, Dikeakos J, Luedemann C, Mach L, Balachandran H, Buzby A, Rao S, Letvin N, Gao Y, Arts EJ, 2016. Pathogenic infection of Rhesus macaques by an evolving SIV-HIV derived from CCR5-using envelope genes of acute HIV-1 infections. Virology 499, 298–312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bomsel M, 1997. Transcytosis of infectious human immunodeficiency virus across a tight human epithelial cell line barrier. Nat. Med. 3, 42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

