Folic acid-functionalized drug delivery platform of resveratrol based on Pluronic 127/D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate mixed micelles
- PMID: 28392687
- PMCID: PMC5373843
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S130094
Folic acid-functionalized drug delivery platform of resveratrol based on Pluronic 127/D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate mixed micelles
Abstract
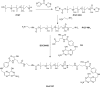
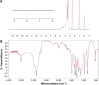
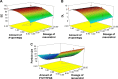
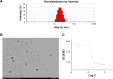
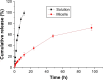
A folic acid (FA)-functionalized drug vehicle platform based on Pluronic 127 (P127)/D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) mixed micelles was orchestrated for an effective delivery of the model drug resveratrol in order to address the problem of poor water solubility and rapid metabolism of resveratrol and improve its targeted accumulation at tumor site. The FA-decorated mixed micelles were prepared using thin-film hydration method and optimized by central composite design approach. The micelles were also characterized in terms of size and morphology, drug entrapment efficiency and in vitro release profile. In addition, the cytotoxicity and cell uptake of the micelles were evaluated in folate receptor-overexpressing MCF-7 cell line. In vivo pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies were also performed. The average size of the micelles was ~20 nm with a spherical shape and high encapsulation efficiency (99.67%). The results of fluorescence microscopy confirmed the targeting capability of FA-conjugated micelles in MCF-7 cells. FA-modified micelles exhibited superior pharmacokinetics in comparison with that of solution. Further, the low accumulation of resveratrol-loaded FA micelles formulation in the heart and kidney avoided toxicity of these vital organs. It could be concluded that folate-modified P127/TPGS mixed micelles might serve as a potential delivery platform for resveratrol.
Keywords: Pluronic 127/TPGS; folic acid conjugation; mixed micelles; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synergistic effect of pH-responsive folate-functionalized poloxamer 407-TPGS-mixed micelles on targeted delivery of anticancer drugs.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Feb 13;10:1321-34. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S78438. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25709451 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced effect of folated pluronic F87-PLA/TPGS mixed micelles on targeted delivery of paclitaxel.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Oct;103:1011-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.136. Epub 2017 May 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28552723
-
Poloxamer 407/TPGS mixed micelles for delivery of gambogic acid to breast and multidrug-resistant cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:713-21. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S28745. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22359450 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation cancer nanotherapeutics: Pluronic® F127 based mixed micelles for enhanced drug delivery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3241-3270. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03582-x. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39527309 Review.
-
The science of resveratrol, formulation, pharmacokinetic barriers and its chemotherapeutic potential.Int J Pharm. 2022 Apr 25;618:121605. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121605. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35227804 Review.
Cited by
-
Folic acid grafted mixed polymeric micelles as a targeted delivery strategy for tamoxifen citrate in treatment of breast cancer.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Apr;14(4):945-958. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01443-3. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37906415 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Study on Pharmacokinetics and Antitumor Pharmacodynamics of Folic Acid Modified Crebanine Polyethyleneglycol-Polylactic Acid Hydroxyacetic Acid Copolymer Nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 17;19:10513-10536. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S477027. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39435040 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-loaded nanomedicines for cancer applications.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021 Jun;4(3):e1353. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1353. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 33655717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triphenylphosphonium and D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-modified, tanshinone IIA-loaded lipid-polymeric nanocarriers for the targeted therapy of myocardial infarction.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jul 10;13:4045-4057. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S165590. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30022826 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-Based Nanoformulations as an Emerging Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 1;8:649395. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.649395. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34540888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amri A, Chaumeil JC, Sfar S, Charrueau C. Administration of resveratrol: what formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J Control Release. 2012;158(2):182–193. - PubMed
-
- Carletto B, Berton J, Ferreira TN, et al. Resveratrol-loaded nanocapsules inhibit murine melanoma tumor growth. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;144:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Liu B, Cailing E, et al. Resveratrol inhibits the proliferation of human melanoma cells by inducing G1/S cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(1):400–404. - PubMed
-
- Summerlin N, Soo E, Thakur S, Qu Z, Jambhrunkar S, Popat A. Resveratrol nanoformulations: challenges and opportunities. Int J Pharm. 2015;479(2):282–290. - PubMed
-
- Pujara N, Jambhrunkar S, Wong KY, McGuckin M, Popat A. Enhanced colloidal stability, solubility and rapid dissolution of resveratrol by nanocomplexation with soy protein isolate. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;488:303–308. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

