Etiology and clinical characteristics of fever of unknown origin in children: a 15-year experience in a single center
- PMID: 28392823
- PMCID: PMC5383636
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.3.77
Etiology and clinical characteristics of fever of unknown origin in children: a 15-year experience in a single center
Abstract
Purpose: Fever is one of the most common symptoms in children. In previous studies, infectious disease was the most common cause of pediatric fever of unknown origin (FUO). The aim of this study is to investigate the etiology, clinical characteristics and prognosis of pediatric FUO in 21 century with more diagnostics available and to analyze the factors for certain disease categories.
Methods: Among the children under 18 years old who were hospitalized at Samsung Medical Center from January 2000 to December 2014, the patients who met the criteria including fever of ≥38.0℃ for longer than ≥14 days and failure to reach a diagnosis after one week of investigations were included.
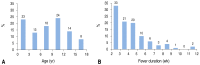
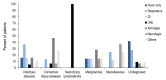
Results: Total 100 patients were identified. Confirmed diagnosis was achieved in 57 patients (57%). Among them, infectious diseases (n=19, 19%) were most common, followed by connective tissue diseases (n=15, 15%), necrotizing lymphadenitis (n=8, 8%), and malignancies (n=7, 7%). Children with fever duration over 28 days had a trend for higher frequency of connective tissue diseases (28.3%) except undiagnosed etiology. The symptoms such as arthritis, lymph node enlargement and only fever without other symptoms were significantly related with connective tissue diseases, necrotizing lymphadenitis and undiagnosed respectively (P<0.001). Ninety-two patients have become afebrile at discharge and 1 patient died (1%).
Conclusion: Almost half of our patients were left without diagnosis. Although it has been known that infectious disease was most common cause of pediatric FUO in the past, undiagnosed portion of FUO have now increased due to development of diagnostic techniques for infectious diseases.
Keywords: Child; Fever of unknown origin; Infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[An analysis of etiologies of fever of unknown origin in 372 patients].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Apr;53(4):298-302. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24857305 Chinese.
-
Clinical analysis of fever of unknown origin in children: A 10-year experience in a northern Taiwan medical center.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017 Feb;50(1):40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017. PMID: 25735796
-
Etiology and Resource Use of Fever of Unknown Origin in Hospitalized Children.Hosp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;8(3):135-140. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2017-0098. Hosp Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29487087
-
Fever in Children and Fever of Unknown Origin.Indian J Pediatr. 2016 Jan;83(1):38-43. doi: 10.1007/s12098-015-1724-4. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Indian J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 25724501 Review.
-
Management of children with prolonged fever of unknown origin and difficulties in the management of fever of unknown origin in children in developing countries.Paediatr Drugs. 2001;3(4):247-62. doi: 10.2165/00128072-200103040-00002. Paediatr Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11354697 Review.
Cited by
-
Key diagnostic characteristics of fever of unknown origin in Japanese patients: a prospective multicentre study.BMJ Open. 2019 Nov 19;9(11):e032059. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032059. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31748308 Free PMC article.
-
Fever of unknown origin: a retrospective review of pediatric patients from an urban, tertiary care center in Washington, DC.World J Pediatr. 2020 Apr;16(2):177-184. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00237-3. Epub 2019 Mar 19. World J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 30888665
-
Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography in Evaluations of Classical Fever of Unknown Origin and Length of Hospitalization: A 10-Year Medical Record Review of a Tertiary Hospital.Infect Chemother. 2023 Mar;55(1):22-28. doi: 10.3947/ic.2022.0082. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Infect Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36372950 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and metagenomic characteristics of lymphadenopathy related to fever of unknown origin in children.Pediatr Res. 2024 Sep;96(4):1037-1044. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03187-3. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 38678116 Free PMC article.
-
Update on Fever of Unknown Origin in Children: Focus on Etiologies and Clinical Approach.Children (Basel). 2023 Dec 24;11(1):20. doi: 10.3390/children11010020. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38255334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chow A, Robinson JL. Fever of unknown origin in children: a systematic review. World J Pediatr. 2011;7:5–10. - PubMed
-
- Park HS, Im SJ, Park SE. Investigation of causes of FUO (fever of unknown origin) in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2006;49:1282–1286.
-
- Antoon JW, Potisek NM, Lohr JA. Pediatric fever of unknown origin. Pediatr Rev. 2015;36:380–390. - PubMed
-
- Dayal R, Agarwal D. Fever in children and fever of unknown origin. Indian J Pediatr. 2016;83:38–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

