Clinical Implications for the Timely Diagnosis of Mycobacterium marinum in the Age of Biologic Therapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 28392952
- PMCID: PMC5368394
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5274302
Clinical Implications for the Timely Diagnosis of Mycobacterium marinum in the Age of Biologic Therapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
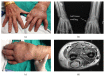
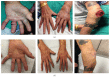
Mycobacterium marinum infections typically present as cutaneous nodular lesions with a sporotrichoid lymphatic spread on extensor surfaces of extremities. The natural history of this infection can be altered if the host is immunosuppressed, leading to disseminated presentations. A detailed exposure history and high degree of suspicion for this indolent pathogen are often required for the correct diagnosis of this disease. We present a case of a 67-year-old male misdiagnosed with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis presenting with rheumatic nodules. Initiation of chronic immunosuppressant therapy including biologic monoclonal antibodies resulted in the exacerbation of initially localized disease to broadly disseminated lymphatic, joint, and myotendinous granulomatous disease and led to delay in the correct diagnosis. Cessation of immunosuppressants, with a prolonged course of antimicrobial therapy and multiple surgical debridements were required for cure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local and disseminated infections caused by Mycobacterium marinum: an unusual cause of subcutaneous nodules.J Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Jun;14(3):156-60. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31817759fe. J Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18525435
-
Mycobacterium marinum infections in transplant recipients: case report and review of the literature.Transpl Infect Dis. 2008 Oct;10(5):358-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00317.x. Epub 2008 May 15. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18482202 Review.
-
Dermoscopy of Mycobacterium marinum Skin infection: A Challenging Diagnosis.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019 Dec;27(4):278-279. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2019. PMID: 31969244
-
Sporotrichoid atypical cutaneous infection caused by Mycobacterium marinum.Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009 Mar;18(1):31-4. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009. PMID: 19350186
-
[Mycobacterium marinum granuloma in a fish fancier. Apropos of a case with sporotrichoid lesions].Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1991 Sep 14;121(37):1340-4. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1991. PMID: 1925464 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Flare or foe? - Mycobacterium marinum infection mimicking rheumatoid arthritis tenosynovitis: case report and literature review.BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Mar 16;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s41927-020-0114-3. eCollection 2020. BMC Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32190818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liao C. H., Lai C. C., Ding L. W., et al. Skin and soft tissue infection caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 2007;11(1):96–102. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

