The inflammatory biomarker YKL-40 decreases stepwise after exercise stress test
- PMID: 28392973
- PMCID: PMC5367501
- DOI: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000073
The inflammatory biomarker YKL-40 decreases stepwise after exercise stress test
Abstract
Background: Serum YKL-40 is an inflammatory biomarker associated with disease activity and mortality in diseases characterized by inflammation such as coronary artery disease (CAD). Exercise has a positive effect on CAD, possibly mediated by a decreased inflammatory activity. This study aimed to compare serial measurements of serum YKL-40 before and after exercise in patients with stable CAD versus controls.
Materials and methods: Eleven patients with stable CAD verified by coronary angiography (>70% stenosis) and 11 patients with a computer tomography angiography with no stenosis or calcification (calcium score=0) (controls) performed a standard clinical maximal exercise test. Serum YKL-40 was measured before exercise, immediately after exercise, and every hour for 6 h.
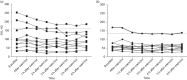
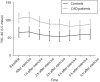
Results: Cardiovascular risk factors were more prevalent among the CAD patients compared with the controls. CAD patients had higher serum concentration of YKL-40 at baseline compared with controls, median (interquartile range) 94 (52-151) versus 57 (45-79) μg/l. Serum YKL-40 decreased stepwise after exercise, with a median decrease of 16 (13-39) μg/l for the CAD patients and 13 (10-22) μg/l for the controls from baseline to the lowest value. Thereafter, values increased again toward baseline level. Time after exercise was a significant factor for decrease in serum YKL-40 (P<0.0001), but no difference in YKL-40 decrease over time could be demonstrated between the groups (P=0.12).
Conclusion: Serum YKL-40 is elevated in patients with documented CAD compared with controls, and it decreases stepwise after exercise in both groups, indicating an anti-inflammatory effect of exercise independent of the presence of coronary atherosclerosis.
Keywords: biomarkers; coronary artery disease; exercise test; inflammation; serum YKL-40; stable angina pectoris.
Figures

References
-
- Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: part I: general considerations, the epidemiologic transition, risk factors, and impact of urbanization. Circulation 2001; 104:2746–2753. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis – an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999; 340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Biasillo G, Leo M, Della BR, Biasucci LM. Inflammatory biomarkers and coronary heart disease: from bench to bedside and back. Intern Emerg Med 2010; 5:225–233. - PubMed
-
- Johansen JS. Studies on serum YKL-40 as a biomarker in diseases with inflammation, tissue remodelling, fibroses and cancer. Dan Med Bull 2006; 53:172–209. - PubMed
-
- Boot RG, van Achterberg TA, van Aken BE, Renkema GH, Jacobs MJ, Aerts JM, de Vries CJ. Strong induction of members of the chitinase family of proteins in atherosclerosis: chitotriosidase and human cartilage gp-39 expressed in lesion macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999; 19:687–694. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
