Anti‑inflammatory effects of dihydromyricetin in a mouse model of asthma
- PMID: 28393183
- PMCID: PMC5436282
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6428
Anti‑inflammatory effects of dihydromyricetin in a mouse model of asthma
Abstract
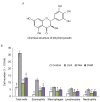
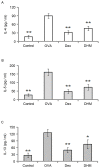
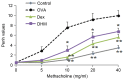
Dihydromyricetin (DHM) is a plant flavonoid and is the primary active ingredient isolated from the medicinal herb, Ampelopsis grossedentata. DHM has been shown to possess various pharmacological activities, including anti‑inflammatory effects. However, the possible role of DHM in asthma treatment remains to be elucidated. The present study aimed to investigate its anti‑inflammatory properties in mice with symptoms of allergic asthma. The C57BL/6 mice were sensitized and challenged with ovalbumin (OVA) to induce asthma. DHM or phosphate‑buffered saline treatment was administered 1 h prior to the OVA challenge. The levels of interleukin (IL)‑4, IL‑5 and IL‑13 in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were measured by enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and OVA‑specific serum IgE and IgG1 levels were also determined by ELISA. Histopathological staining was performed to evaluate the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the BAL fluid, lung tissues and goblet cell hyperplasia. DHM treatment significantly reduced the total number of inflammatory cells, including eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes and macrophages, in the BAL fluid. DHM also reduced the levels of IL‑4, IL‑5 and IL‑13 in the BAL fluid, and reduced the secretion of OVA‑specific IgE and IgG1 in the serum. The histological staining demonstrated that DHM treatment effectively suppressed the OVA‑induced inflammatory cells in the lung tissues and in the mucus hypersecreted by goblet cells in the airway. These results showed that DHM had a potent anti‑inflammatory effect in an OVA‑induced mouse model of asthma, offering potential as an anti‑inflammatory agent for the treatment of asthma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro anti‑allergic and anti‑inflammatory effects of Dryopteris crassirhizoma through the modulation of the NF‑ĸB signaling pathway in an ovalbumin‑induced allergic asthma mouse model.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):3597-3606. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11460. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33000211 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of simvastatin in mouse allergic asthma model.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Feb 14;557(1):76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.11.027. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17169357
-
Saponin-enriched extract of Asparagus cochinchinensis alleviates airway inflammation and remodeling in ovalbumin-induced asthma model.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Nov;40(5):1365-1376. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3147. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28949387 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydromyricetin Acts as a Potential Redox Balance Mediator in Cancer Chemoprevention.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Mar 11;2021:6692579. doi: 10.1155/2021/6692579. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33776577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-32: its role in asthma and potential as a therapeutic agent.Respir Res. 2018 Jun 25;19(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0832-x. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29940981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dihydromyricetin promotes autophagy and attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating miR-155-5p/PTEN signaling in diabetic nephropathy.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Aug 3;20(3):372-380. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2019.4410. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31668144 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydromyricetin induces apoptosis in a human choriocarcinoma cell line.Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):4229-4234. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9220. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30214558 Free PMC article.
-
Annotation of genes involved in high level of dihydromyricetin production in vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) by transcriptome analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Mar 30;20(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2324-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32228461 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Dihydromyricetin on Inflammatory Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 18;12:794563. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.794563. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35115939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dihydromyricetin functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatoblastoma by regulating SOD1/ROS pathway.Front Oncol. 2023 May 15;13:1160548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1160548. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37256172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee SH, Kim DW, Kim HR, Woo SJ, Kim SM, Jo HS, Jeon SG, Cho SW, Park JH, Won MH, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Tat-Annexin protein on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in a mouse model of asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417:1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.084. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murad HA, Hasanin AH. The anti-inflammatory effects of 1,1 dimethyl-4-phenylpiperazinium (DMPP) compared to dexamethasone in a guinea pig model of ovalbumin induced asthma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:2228–2236. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

