A heptameric peptide purified from Spirulina sp. gastrointestinal hydrolysate inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme- and angiotensin II-induced vascular dysfunction in human endothelial cells
- PMID: 28393188
- PMCID: PMC5403476
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2941
A heptameric peptide purified from Spirulina sp. gastrointestinal hydrolysate inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme- and angiotensin II-induced vascular dysfunction in human endothelial cells
Abstract
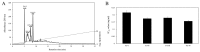
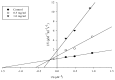
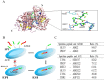
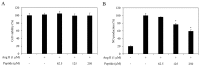
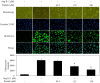
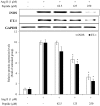
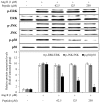
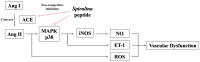
In this study, a marine microalga Spirulina sp.-derived protein was hydrolyzed using gastrointestinal enzymes to produce an angiotensin I (Ang I)-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide. Following consecutive purification, the potent ACE inhibitory peptide was composed of 7 amino acids, Thr-Met‑Glu‑Pro‑Gly‑Lys-Pro (molecular weight, 759 Da). Analysis using the Lineweaver-Burk plot and molecular modeling suggested that the purified peptide acted as a mixed non-competitive inhibitor of ACE. The inhibitory effects of the peptide against the cellular production of vascular dysfunction-related factors induced by Ang II were also investigated. In human endothelial cells, the Ang II-induced production of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species was inhibited, and the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) was downregulated when the cells were cultured with the purified peptide. Moreover, the peptide blocked the activation of p38 mitogen‑activated protein kinase. These results indicated that this Spirulina sp.-derived peptide warrants further investigation as a potential pharmacological inhibitor of ACE and vascular dysfunction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from the rotifer, Brachionus rotundiformis.Bioresour Technol. 2009 Nov;100(21):5255-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.057. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Bioresour Technol. 2009. PMID: 19540110
-
Naturally occurring angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from a fertilized egg and its inhibitory mechanism.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jun 18;62(24):5500-6. doi: 10.1021/jf501368a. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24866326
-
Analysis of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease-hydrolyzed marine shrimp Acetes chinensis.J Pept Sci. 2006 Nov;12(11):726-33. doi: 10.1002/psc.789. J Pept Sci. 2006. PMID: 16981241
-
Plant food-derived Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides.J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jun 24;57(12):5113-20. doi: 10.1021/jf900494d. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. PMID: 19449887 Review.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins: biochemistry, bioactivity and production.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(8):773-91. doi: 10.2174/138161207780363068. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17430180 Review.
Cited by
-
The Antihypertensive Effects and Potential Molecular Mechanism of Microalgal Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Like Peptides: A Mini Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4068. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084068. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purification and Molecular Docking Study on the Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptide Isolated from Hydrolysates of the Deep-Sea Mussel Gigantidas vrijenhoeki.Mar Drugs. 2023 Aug 21;21(8):458. doi: 10.3390/md21080458. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37623739 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in the production and utilization of photosynthetic microorganisms for food applications.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 22;9(4):e14708. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14708. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37151658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Spirulina Aqueous Extract on Vasodilator Function of Arteries from Hypertensive Rats.Int J Vasc Med. 2020 Dec 8;2020:6657077. doi: 10.1155/2020/6657077. eCollection 2020. Int J Vasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33457015 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Allergic Effect of Low Molecular Weight Digest from Abalone Viscera on Atopic Dermatitis-Induced NC/Nga.Mar Drugs. 2021 Nov 12;19(11):634. doi: 10.3390/md19110634. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34822505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamada Y, Kato K, Yoshida T, Yokoi K, Matsuo H, Watanabe S, Ichihara S, Metoki N, Yoshida H, Satoh K, et al. Association of polymorphisms of ABCA1 and ROS1 with hypertension in Japanese individuals. Int J Mol Med. 2008;21:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Ko SC, Jung WK, Kang SM, Lee SH, Kang MC, Heo SJ, Kang KH, Kim YT, Park SJ, Jeong Y, et al. Angio-tensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition and nitric oxide (NO)-mediated antihypertensive effect of octaphlorethol A isolated from Ishige sinicola: in vitro molecular mechanism and in vivo SHR model. J Funct Foods. 2016;18:289–299. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.07.003. - DOI
-
- Ahn CB, Jeon YJ, Kim YT, Je JY. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by alcalase hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2012;47:2240–2245. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2012.08.019. - DOI
-
- Tomita N, Yamasaki K, Izawa K, Kunugiza Y, Osako MK, Ogihara T, Morishita R. Improvement of organ damage by a non-depressor dose of imidapril in diabetic spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Mol Med. 2007;19:571–579. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

