Psoriasin promotes invasion, aggregation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells; association with disease progression
- PMID: 28393239
- PMCID: PMC5403466
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3953
Psoriasin promotes invasion, aggregation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells; association with disease progression
Abstract
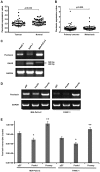
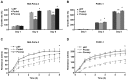
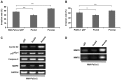
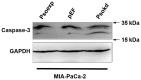
Psoriasin (S100A7) is an 11-kDa small calcium binding protein initially isolated from psoriatic skin lesions. It belongs to the S100 family of proteins which play an important role in a range of cell functions including proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis. Aberrant Psoriasin expression has been implicated in a range of cancers and is often associated with poor prognosis. This study examined the role of Psoriasin on pancreatic cancer cell functions and the implication in progression of the disease. Expression of Psoriasin was determined in a cohort of pancreatic tissues comprised of 126 pancreatic tumours and 114 adjacent non-tumour pancreatic tissues. Knockdown and overexpression of Psoriasin in pancreatic cancer cells was performed using specifically constructed plasmids, which either had anti-Psoriasin ribozyme transgene or the full length human Psoriasin coding sequence. Psoriasin knockdown and overexpression was verified using conventional RT-PCR and qPCR. The effect of manipulating Psoriasin expression on pancreatic cancer cell functions was assessed using several in vitro cell function assays. Local invasive pancreatic cancers extended beyond the pancreas expressed higher levels of Psoriasin transcripts compared with the cancers confined to the pancreas. Primary tumours with distant metastases exhibited a reduced expression of Psoriasin. Psoriasin overexpression cell lines exhibited significantly increased growth and migration compared to control cells. In addition, Psoriasin overexpression resulted in increased pancreatic cancer cell invasion which was associated with upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9. Overexpression of Psoriasin also promoted aggregation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells when they lost anchorage. Taken together, higher expression of Psoriasin was associated with local invasion in pancreatic cancers. Psoriasin expression is associated with pancreatic cancer cell growth, migration, cell-matrix adhesion, and invasion via regulation of MMPs. As such, the proposed implications of Psoriasin in invasion, disease progression and as a potential therapeutic target warrant further investigation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased expression of Psoriasin is correlated with poor prognosis of bladder transitional cell carcinoma by promoting invasion and proliferation.Oncol Rep. 2020 Feb;43(2):562-570. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7445. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31894335 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasin (S100A7) is a positive regulator of survival and invasion of prostate cancer cells.Urol Oncol. 2013 Nov;31(8):1576-83. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22694938
-
Psoriasin overexpression confers drug resistance to cisplatin by activating ERK in gastric cancer.Int J Oncol. 2018 Sep;53(3):1171-1182. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4455. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29956751
-
Psoriasin, a multifunctional player in different diseases.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014;15(8):836-42. doi: 10.2174/138920371508141128152712. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014. PMID: 25466546 Review.
-
Opposing functions of psoriasin (S100A7) and koebnerisin (S100A15) in epithelial carcinogenesis.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;13(4):588-94. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 May 9. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23664757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chrysophanol exhibits anti-cancer activities in lung cancer cell through regulating ROS/HIF-1a/VEGF signaling pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;393(3):469-480. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01746-8. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. Retraction in: Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2021 Mar;394(3):577-578. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-02019-5. PMID: 31655854 Retracted.
-
Association of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) with Cisplatin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 3;21(11):4002. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114002. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32503307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100s and HMGB1 Crosstalk in Pancreatic Cancer Tumors.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 28;13(8):1175. doi: 10.3390/biom13081175. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37627239 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Skin Lesions of Patients with Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma.Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Jan 7;100(1):adv00017. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3372. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020. PMID: 31742644 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of Psoriasin is correlated with poor prognosis of bladder transitional cell carcinoma by promoting invasion and proliferation.Oncol Rep. 2020 Feb;43(2):562-570. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7445. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31894335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Leffers H, Honoré B, Dejgaard K, Olsen E, Kiil J, Walbum E, Andersen AH, Basse B, et al. Molecular cloning, occurrence, and expression of a novel partially secreted protein “psoriasin” that is highly up-regulated in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991;97:701–712. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wolf R, Howard OM, Dong H-F, Voscopoulos C, Boeshans K, Winston J, Divi R, Gunsior M, Goldsmith P, Ahvazi B, et al. Chemotactic activity of S100A7 (Psoriasin) is mediated by the receptor for advanced glycation end products and potentiates inflammation with highly homologous but functionally distinct S100A15. J Immunol. 2008;181:1499–1506. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.1499. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

