Decreased feedback learning in anorexia nervosa persists after weight restoration
- PMID: 28393399
- PMCID: PMC5869029
- DOI: 10.1002/eat.22709
Decreased feedback learning in anorexia nervosa persists after weight restoration
Abstract
Objective: Anorexia Nervosa (AN) is a serious disorder, with a mortality rate the highest of any psychiatric illness. It is notoriously challenging to treat and mechanisms of illness are not well understood. Reward system abnormalities have been proposed across theoretical models of the persistence of AN. Feedback learning is an important component of how reward systems shape behavior and we hypothesized that individuals with AN would show poorer learning from feedback.
Methods: We administered the acquired equivalence task to measure both learning from incremental feedback and generalization of that learning to novel stimuli. Participants were individuals with AN (n = 36) before and after intensive weight restoration treatment and healthy comparison participants (HC, n = 26) tested twice. Performance was assessed as accuracy during the Learning and Test phases, for both trained and novel stimuli. The relationship between task performance and eating disorder severity at baseline was also assessed.
Results: Both before and after treatment, individuals with AN showed reduced learning from feedback in the Learning phase (F3,180 = 2.75, p = .048) and lower accuracy during the Test phase (F1,60 = 4.29, p = .043), as compared with HC. Individuals with AN did not differ from HC in accuracy for novel stimuli (F1,60 = 1.04, p = .312), indicating no deficit in generalization. Decreased acquisition of feedback learning was associated with longer illness duration and with greater eating disorder symptom severity at baseline.
Conclusions: Individuals with AN show reduced learning from feedback or reinforcement, which may contribute to difficulties in changing maladaptive behaviors.
Keywords: acquired equivalence; anorexia nervosa; cognitive neuroscience; eating disorders; feedback learning; longitudinal; neuropsychology; reward.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

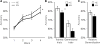

References
-
- Arcelus J, Mitchell AJ, Wales J, Nielsen S. Mortality Rates in Patients With Anorexia Nervosa and Other Eating Disorders: A Meta-analysis of 36 Studies. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2011;68(7):724–31. - PubMed
-
- Rosling AM, Sparen P, Norring C, von Knorring AL. Mortality of eating disorders: a follow-up study of treatment in a specialist unit 1974-2000. Int J Eat Disord. 2011;44(4):304–10. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders FE. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Watson HJ, Bulik CM. Update on the treatment of anorexia nervosa: review of clinical trials, practice guidelines and emerging interventions. Psychological medicine. 2013;43(12):2477–500. - PubMed
-
- Pike KM. Long-term course of anorexia nervosa: response, relapse, remission, and recovery. Clin Psychol Rev. 1998;18(4):447–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

