Prosthetic joint and implant contamination caused by Ralstonia pickettii: a report of three cases٭
- PMID: 28393758
- PMCID: PMC5385672
- DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017017
Prosthetic joint and implant contamination caused by Ralstonia pickettii: a report of three cases٭
Abstract
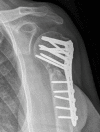
We describe three cases of orthopaedic contamination caused by Ralstonia pickettii grown from prosthetic joint and implant material cultures following sonication in the microbiology laboratory. Given the temporal association between the cases, lack of clinical or intra-operative features of infection, growth of the organism in the water bath, and unlikely etiology of Ralstonia as a prosthetic joint or implant pathogen, the bacteria were judged to be contaminants.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2017.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sonication contribution to identifying prosthetic joint infection with Ralstonia pickettii: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jul 19;18(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1678-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28724376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ralstonia pickettii: a persistent gram-negative nosocomial infectious organism.J Hosp Infect. 2006 Mar;62(3):278-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2005.08.015. Epub 2005 Dec 6. J Hosp Infect. 2006. PMID: 16337309 Review.
-
Ralstonia pickettii Bacteremia: An Emerging Infection in a Tertiary Care Hospital Setting.Cureus. 2019 Jul 5;11(7):e5084. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5084. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31516793 Free PMC article.
-
PVC-piping promotes growth of Ralstonia pickettii in dialysis water treatment facilities.Water Sci Technol. 2013;68(4):929-33. doi: 10.2166/wst.2013.332. Water Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23985526
-
Ralstonia pickettii bacteremia in hemodialysis patients: a report of two cases.Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016 Jun;28(2):195-8. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20160033. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016. PMID: 27410414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Updegrove GF, Armstrong AD, Kim HMM (2015) Preoperative and intraoperative infection workup in apparently aseptic revision shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24(3), 491–500. - PubMed
-
- Dapunt U, Lehner B, Burckhardt I, Zimmermann S, Hänsch GM, Ewerbeck V (2014) Evaluation of implant sonication as a diagnostic tool in implant-associated infections. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater 12(3), 135–140. - PubMed
-
- Trampuz A, Piper KE, Jacobson MJ, Hanssen AD, Unni KK, Osmon DR, Mandrekar JN, Cockerill FR, Steckelberg JM, Greenleaf JF, et al. (2007) Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N Engl J Med 357(7), 654–663. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
