Medium-term impact of the economic crisis on mortality, health-related behaviours and access to healthcare in Greece
- PMID: 28393903
- PMCID: PMC5385490
- DOI: 10.1038/srep46423
Medium-term impact of the economic crisis on mortality, health-related behaviours and access to healthcare in Greece
Abstract
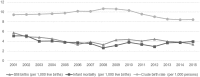
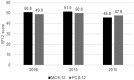
Previous studies on the health consequences of the crisis in Greece investigated short-term impacts on selected outcomes. This study examined the impact of the crisis on a key set of health indicators with longer follow up than previous studies. We conducted interrupted time series (ITS) analysis to compare trends in standardised mortality by cause before and during the crisis. We examined changes in fruit and vegetable consumption, smoking, physical activity, obesity, out-of-pocket payments and unmet needs for healthcare using national household data from the "Hellas Health" surveys. Standardised mortality rates for suicides (p < 0.001) and infant mortality (p = 0.003) increased during the crisis compared to pre-existing trends, while mortality from respiratory diseases (p = 0.053) and transport accidents (p = 0.067) decreased. The prevalence of smoking (42.6% to 36.5%; RR = 0.86) and sedentary lifestyle (43.4% to 29.0%; RR = 0.69) declined. The prevalence of unmet need for healthcare significantly increased from 10.0% to 21.9% (RR = 2.10) and the proportion of people paying out-of-pocket for healthcare from 34.4% to 58.7% (RR = 1.69) between 2010 and 2015. The impact of the economic crisis in Greece on health was more nuanced than previous reports suggest. Effective strategies to mitigate the adverse health impacts of economic crises need to be better understood and implemented.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Katsimi M. & Moutos T. EMU and the Greek crisis The political-economy perspective. Eur J Polit Econ 26, 568–576, doi: 10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2010.08.002 (2010). - DOI
-
- Hellenic Statistical Authority Statistics. www.statistics.gr (Date of access: 20/01/2017) (2016).
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development OECD data. https://data.oecd.org (Date of access: 18/10/2016) (2016).
-
- Hellenic Statistical Authority Living Conditions in Greece. www.statistics.gr/en/living-conditions-in-greece (Date of access: 18/10/2016) (2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

