Demonstration of nanoimprinted hyperlens array for high-throughput sub-diffraction imaging
- PMID: 28393906
- PMCID: PMC5385565
- DOI: 10.1038/srep46314
Demonstration of nanoimprinted hyperlens array for high-throughput sub-diffraction imaging
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Demonstration of nanoimprinted hyperlens array for high-throughput sub-diffraction imaging.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 24;7:46895. doi: 10.1038/srep46895. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28836623 Free PMC article.
Abstract
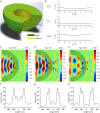
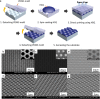
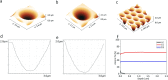
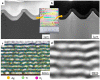
Overcoming the resolution limit of conventional optics is regarded as the most important issue in optical imaging science and technology. Although hyperlenses, super-resolution imaging devices based on highly anisotropic dispersion relations that allow the access of high-wavevector components, have recently achieved far-field sub-diffraction imaging in real-time, the previously demonstrated devices have suffered from the extreme difficulties of both the fabrication process and the non-artificial objects placement. This results in restrictions on the practical applications of the hyperlens devices. While implementing large-scale hyperlens arrays in conventional microscopy is desirable to solve such issues, it has not been feasible to fabricate such large-scale hyperlens array with the previously used nanofabrication methods. Here, we suggest a scalable and reliable fabrication process of a large-scale hyperlens device based on direct pattern transfer techniques. We fabricate a 5 cm × 5 cm size hyperlenses array and experimentally demonstrate that it can resolve sub-diffraction features down to 160 nm under 410 nm wavelength visible light. The array-based hyperlens device will provide a simple solution for much more practical far-field and real-time super-resolution imaging which can be widely used in optics, biology, medical science, nanotechnology and other closely related interdisciplinary fields.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abbe E. Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Archiv für mikroskopische Anatomie 9, 413–418 (1873).
-
- Hillenbrand R. & Keilmann F. Optical oscillation modes of plasmon particles observed in direct space by phase-contrast near-field microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 73, 239–243 (2001).
-
- Betzig E., Trautman J. K., Harris T. D., Weiner J. S. & Kostelak R. L. Breaking the diffraction barrier: Optical microscopy on a nanometric scale. Science 251, 1468–1470 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Hell S. W. Toward fluorescence nanoscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1347–1355 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

