Altered B cell signalling in autoimmunity
- PMID: 28393923
- PMCID: PMC5523822
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.24
Altered B cell signalling in autoimmunity
Abstract
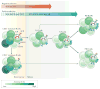
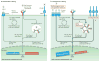
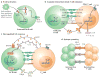
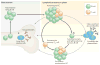
Recent work has provided new insights into how altered B cell-intrinsic signals - through the B cell receptor (BCR) and key co-receptors - function together to promote the pathogenesis of autoimmunity. These combined signals affect B cells at two distinct stages: first, in the selection of the naive repertoire; and second, during extrafollicular or germinal centre activation responses. Thus, dysregulated signalling can lead to both an altered naive BCR repertoire and the generation of autoantibody-producing B cells. Strikingly, high-affinity autoantibodies predate and predict disease in several autoimmune disorders, including type 1 diabetes and systemic lupus erythematosus. This Review summarizes how, rather than being a downstream consequence of autoreactive T cell activation, dysregulated B cell signalling can function as a primary driver of many human autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

