Quantitative analysis of the tomato nuclear proteome during Phytophthora capsici infection unveils regulators of immunity
- PMID: 28394025
- PMCID: PMC5637918
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.14540
Quantitative analysis of the tomato nuclear proteome during Phytophthora capsici infection unveils regulators of immunity
Abstract
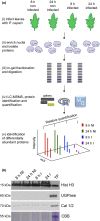
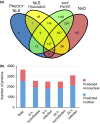
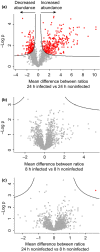
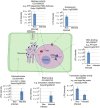
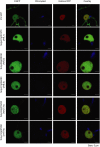
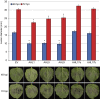
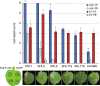
Plant-pathogen interactions are complex associations driven by the interplay of host and microbe-encoded factors. With secreted pathogen proteins (effectors) and immune signalling components found in the plant nucleus, this compartment is a battleground where susceptibility is specified. We hypothesized that, by defining changes in the nuclear proteome during infection, we can pinpoint vital components required for immunity or susceptibility. We tested this hypothesis by documenting dynamic changes in the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) nuclear proteome during infection by the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora capsici. We enriched nuclei from infected and noninfected tissues and quantitatively assessed changes in the nuclear proteome. We then tested the role of candidate regulators in immunity through functional assays. We demonstrated that the host nuclear proteome dynamically changes during P. capsici infection. We observed that known nuclear immunity factors were differentially expressed and, based on this observation, selected a set of candidate regulators that we successfully implicated in immunity to P. capsici. Our work exemplifies a powerful strategy to gain rapid insight into important nuclear processes that underpin complex crop traits such as resistance. We have identified a large set of candidate nuclear factors that may underpin immunity to pathogens in crops.
Keywords: Phytophthora; immunity; nucleus; plant-microbe interactions; quantitative proteomics; tomato.
© 2017 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2017 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures
References
-
- Bos JIB, Armstrong MR, Gilroy EM, Boevink PC, Hein I, Taylor RM, Tian ZD, Engelhardt S, Vetukuri RR, Harrower B et al 2010. Phytophthora infestans effector AVR3a is essential for virulence and manipulates plant immunity by stabilizing host E3 ligase CMPG1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 107: 9909–9914. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

