Personalised asthma action plans for adults with asthma
- PMID: 28394084
- PMCID: PMC6478068
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011859.pub2
Personalised asthma action plans for adults with asthma
Abstract
Background: A key aim of asthma care is to empower each person to take control of his or her own condition. A personalised asthma action plan (PAAP), also known as a written action plan, an individualised action plan, or a self-management action plan, contributes to this endeavour. A PAAP includes individualised self-management instructions devised collaboratively with the patient to help maintain asthma control and regain control in the event of an exacerbation. A PAAP includes baseline characteristics (such as lung function), maintenance medication and instructions on how to respond to increasing symptoms and when to seek medical help.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of PAAPs used alone or in combination with education, for patient-reported outcomes, resource use and safety among adults with asthma.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Airways Group Specialised Register of trials, clinical trial registers, reference lists of included studies and review articles, and relevant manufacturers' websites up to 14 September 2016.
Selection criteria: We included parallel randomised controlled trials (RCTs), both blinded and unblinded, that evaluated written PAAPs in adults with asthma. Included studies compared PAAP alone versus no PAAP, and/or PAAP plus education versus education alone.
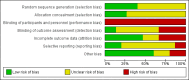
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted study characteristics and outcome data and assessed risk of bias for each included study. Primary outcomes were number of participants reporting at least one exacerbation requiring an emergency department (ED) visit or hospitalisation, asthma symptom scores on a validated scale and adverse events (all causes). Secondary outcomes were quality of life measured on a validated scale, number of participants reporting at least one exacerbation requiring systemic corticosteroids, respiratory function and days lost from work or study. We used a random-effects model for all analyses and standard Cochrane methods throughout.
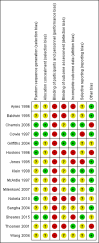
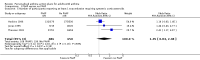
Main results: We identified 15 studies described in 27 articles that met our inclusion criteria. These 15 included studies randomised a total of 3062 participants (PAAP vs no PAAP: 2602 participants; PAAP plus education vs education alone: 460 participants). Ten studies (eight PAAP vs no PAAP; two PAAP plus education vs education alone) provided outcome data that contributed to quantitative analyses. The overall quality of evidence was rated as low or very low.Fourteen studies lasted six months or longer, and the remaining study lasted for 14 weeks. When reported, mean age ranged from 22 to 49 years and asthma severity ranged from mild to severe/high risk. PAAP alone compared with no PAAPResults showed no clear benefit or harm associated with PAAPs in terms of the number of participants requiring an ED visit or hospitalisation for an exacerbation (odds ratio (OR) 0.75, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.45 to 1.24; 1385 participants; five studies; low-quality evidence), change from baseline in asthma symptoms (mean difference (MD) -0.16, 95% CI -0.25 to - 0.07; 141 participants; one study; low-quality evidence) or the number of serious adverse events, including death (OR 3.26, 95% CI 0.33 to 32.21; 125 participants; one study; very low-quality evidence). Data revealed a statistically significant improvement in quality of life scores for those receiving PAAP compared with no PAAP (MD 0.18, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.30; 441 participants; three studies; low-quality evidence), but this was below the threshold for a minimum clinically important difference (MCID). Results also showed no clear benefit or harm associated with PAAPs on the number of participants reporting at least one exacerbation requiring oral corticosteroids (OR 1.45, 95% CI 0.84 to 2.48; 1136 participants; three studies; very low-quality evidence) nor on respiratory function (change from baseline forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1): MD -0.04 L, 95% CI -0.25L to 0.17 L; 392 participants; three studies; low-quality evidence). In one study, PAAPs were associated with significantly fewer days lost from work or study (MD -6.20, 95% CI -7.32 to - 5.08; 74 participants; low-quality evidence). PAAP plus education compared with education aloneResults showed no clear benefit or harm associated with adding a PAAP to education in terms of the number of participants requiring an ED visit or hospitalisation for an exacerbation (OR 1.08, 95% CI 0.27 to 4.32; 70 participants; one study; very low-quality evidence), change from baseline in asthma symptoms (MD -0.10, 95% CI -0.54 to 0.34; 70 participants; one study; low-quality evidence), change in quality of life scores from baseline (MD 0.13, 95% CI -0.13 to 0.39; 174 participants; one study; low-quality evidence) and number of participants requiring oral corticosteroids for an exacerbation (OR 0.28, 95% CI 0.07 to 1.12; 70 participants; one study; very low-quality evidence). No studies reported serious adverse events, respiratory function or days lost from work or study.
Authors' conclusions: Analysis of available studies was limited by variable reporting of primary and secondary outcomes; therefore, it is difficult to draw firm conclusions related to the effectiveness of PAAPs in the management of adult asthma. We found no evidence from randomised controlled trials of additional benefit or harm associated with use of PAAP versus no PAAP, or PAAP plus education versus education alone, but we considered the quality of the evidence to be low or very low, meaning that we cannot be confident in the magnitude or direction of reported treatment effects. In the context of this caveat, we found no observable effect on the primary outcomes of hospital attendance with an asthma exacerbation, asthma symptom scores or adverse events. We recommend further research with a particular focus on key patient-relevant outcomes, including exacerbation frequency and quality of life, in a broad spectrum of adults, including those over 60 years of age.
Conflict of interest statement
David Evans: provides freelance medical writing services to medical communications agencies.
Alison Rushton: undertook a feasibility study to pilot a locally developed asthma self‐management plan for children and young people within a Clinical Commissioning Group (CCG) locality in the northwest of England. The project was completed in 2015 as part of a Clinical Academic Internship, funded by Health Education England and a northwest CCG. The intern received no payment for including individuals in the study.
Nathan Halcovitch: none.
Fiona Eccles: none.
Timothy Gatheral: none.
Sally Spencer: serves as co‐investigator on the Cochrane Programme Grant supporting this review.
Gemma Whiteley: none.
Caroline Mulvaney: none.
Figures


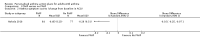










Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ayres 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ayres JG, Campbell LM. A controlled assessment of an asthma self‐management plan involving a budesonide dose regimen. OPTIONS Research Group. European Respiratory Journal 1996;9:886‐92. - PubMed
Baldwin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Baldwin D, Pathak U, King R, Vase B, Pantin C. Outcome of asthmatics attending asthma clinics using self management plans in general practice. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1995;25:454.
-
- Baldwin DR, Pathak UA, King R, Vase BC, Pantin CF. Outcome of asthmatics attending asthma clinics utilising self‐management plans in general practice. Asthma in General Practice 1997;5(2):31‐3.
Charrois 2006 {published data only}
-
- Charrois T, Newman S, Sin D, Senthilselvan A, Tsuyuki RT. Improving asthma symptom control in rural communities: the design of the Better Respiratory Education and Asthma Treatment in Hinton and Edson study. Controlled Clinical Trials 2004;25(5):502‐14. [PUBMED: 15465619] - PubMed
-
- Charrois TL, Newman SC, Senthilselvan A, Tsuyuki RT. Improving asthma control in the rural setting: the BREATHE (Better Respiratory Education and Asthma Treatment in Hinton and Edson) study. Canadian Pharmacists Journal 2006;139:44‐50.
Cowie 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cowie RL, Revitt SG, Underwood MF, Field SK. The effect of a peak flow‐based action plan in the prevention of exacerbations of asthma. Chest 1997;112:1534‐8. - PubMed
Griffiths 2004 {published data only}
Hoskins 1996 {published data only}
Jones 1995 {published data only}
Klein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Klein JJ, Palen J, Kerkhoff AHM. Additional benefit from adding self‐treatment guidelines to a self‐management program for asthma? [abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1998;157:A737.
-
- Klein JJ, Palen J, Uil SM, Zielhuis GA, Seydel ER, Herwaarden CL, et al. Benefit from the inclusion of self‐treatment guidelines to a self‐management programme for adults with asthma. European Respiratory Journal 2001;17:386‐94. - PubMed
-
- Palen J, Klein JJ, Zielhuis GA, Herwaarden CLA, Seydel ER. Behavioural effect of self‐treatment guidelines in a self‐management program for adults with asthma. Patient Education and Counseling 2001;43:161‐9. - PubMed
McArdle 1997 {published data only}
-
- McArdle N, Graham N, Allen C, Tarala R. Patients do not adhere to asthma management plans: information from a controlled study. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1997;27:266.
Milenković 2007 {published data only}
-
- Milenković B, Bosnjak‐Petroić V. [Self‐management program in treatment of asthma]. Srpski Arhiv za Celokupno Lekarstvo 2007;135(3‐4):147‐52. - PubMed
-
- Milenković BA, Stanković IJ, Ilić AM, Petrović VI. Peak expiratory flow‐guided self‐management treatment of asthma in Serbia. Journal of Asthma 2007;44(9):699‐704. - PubMed
Nokela 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nokela M, Arnlind MH, Ehrs PO, Krakau I, Forslund L, Jonsson EW. The influence of structured information and monitoring on the outcome of asthma treatment in primary care: a cluster randomized study. Respiration 2010;79:388‐94. - PubMed
Sangha 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sangha HS, Kapoor BK, Kishan J. Effectiveness of self management plan of bronchial asthma using peak flow meter and symptom profile: a randomized controlled study. Chest 2004;126:706S‐b.
Sheares 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT00149461. Written asthma actions plans versus no written instructions in specialty care. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00149461 (first received 6 September 2005).
-
- Sheares BJ, Evans D. Do patients of specialist physicians really benefit from the use of a written asthma action plan?. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2013;187:A6012.
Thoonen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Schermer TR, Thoonen BP, Boom G, Akkermans RP, Grol RP, Folgering HT, et al. Randomized controlled economic evaluation of asthma self‐management in primary health care. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;166:1062‐72. - PubMed
-
- Schermer TRJ, Thoonen BPA, Boom G, Grol R, Folgering H, Weel C, et al. A randomised controlled economic evaluation of asthma self‐management and usual care in general practice. European Respiratory Journal 2001;18:518s.
-
- Thoonen B, Schermer T, Wel C, Grol R, Schayck C. Clinical effectiveness of self management of asthma in general practice: a randomised controlled trial. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2002;11:73.
-
- Thoonen BP, Schermer TR, Weel C, Grol R, Schayck CP. Clinical effectiveness of self management of asthma in general practice: a randomised controlled trial. International Primary Care Respiratory Group Congress. 2002:92.
Wang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang J, Law B, Ip M, Wu A, Wong M, Lam B, et al. Effect of asthma self management programme on asthma morbidity and health care utilization in adult patients admitted to hospital with acute asthma in Hong Kong: a randomised controlled trial. Respirology 2004;9:A84.
References to studies excluded from this review
Adams 2001 {published data only}
-
- Adams RJ, Boath K, Homan S, Campbell DA, Ruffin RE. A randomized trial of peak‐flow and symptom‐based action plans in adults with moderate‐to‐severe asthma. Respirology 2001;6(4):297‐304. - PubMed
Araújo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Araújo L, Jacinto T, Moreira A, Castel‐Branco MG, Delgado L, Costa‐Pereira A, et al. Clinical efficacy of web‐based versus standard asthma self‐management. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology 2012;22(1):28‐34. - PubMed
Arguel 2013 {published data only}
Bailey 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bailey WC, Richards JM Jr, Brooks CM, Soong SJ, Windsor RA, Manzella BA. A randomized trial to improve self‐management practices of adults with asthma. Archives of Internal Medicine 1990;150(8):1664‐8. - PubMed
Bailey 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bailey WC, Kohler CL, Richards JM, Windsor RA, Brooks CM, Gerald LB, et al. Asthma self‐management: do patient education programs always have an impact?. Archives of Internal Medicine 1999;159(20):2422‐8. - PubMed
Behera 2006 {published data only}
-
- Behera D, Kaur S, Gupta D, Verma SK. Evaluation of self‐care manual in bronchial asthma. Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences 2006;48:43‐8. - PubMed
Behera 2008 {published data only}
-
- Behera D, Kaur S, Gupta D, Verma SK. Avoidance of allergens by the patients with bronchial asthma. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2008;56:325‐8. - PubMed
Berg 1996 {published data only}
-
- Berg J. An evaluation of a self‐management program for adults with asthma. Dissertation Abstracts International 1996;57:1‐B.
-
- Berg J, Dunbar‐Jacob J, Sereika SM. An evaluation of a self‐management program for adults with asthma. Clinical Nursing Research 1997;6(3):225‐38. - PubMed
Boath 1998 {published data only}
-
- Boath K, Homan S, Adams R, Campbell D. Written action plans for asthma; symptoms or peak flow based?. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1998;28:256.
Breysse 2011 {published data only}
Buist 2001 {published data only}
-
- Buist AS. Does shared decision‐making improve asthma outcomes?. CRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) 2001.
Calhoun 2012 {published data only}
-
- Calhoun WJ, Ameredes BT, King TS, Icitovic N, Bleecker ER, Castro M, et al. Comparison of physician‐, biomarker‐, and symptom‐based strategies for adjustment of inhaled corticosteroid therapy in adults with asthma: the BASALT randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 2012;308(10):987‐97. - PMC - PubMed
Chenu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Chenu Eproust A, Cagnioncle O, Frachon I, Guillou B, Dewitte JD, Quiot JJ, et al. Effect of an individualized educational program following treatment optimization in asthmatic adults [abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;161(Suppl 3):A903.
Clark 2005 {published data only}
-
- Clark N. The effect of self‐regulatory education on women with asthma. ClinicalTrials.gov [http://clinicaltrials.gov] 2005.
Cleland 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cleland A, Hall S, Price D. Feasibility of using routine data to identify patients and outcomes for a clinical trial: a randomised controlled trial of asthma self‐management plans in primary care [Abstract]. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2004;13:106 ABS002‐.
Côté 2001 {published data only}
-
- Côté J, Bowie DM, Robichaud P, Parent JG, Battisti L, Boulet LP. Evaluation of two different educational interventions for adult patients consulting with an acute asthma exacerbation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;163(6):1415‐9. - PubMed
Couturaud 2002 {published data only}
-
- Couturaud F, Proust A, Frachon I, Dewitte JD, Oger E, Quiot JJ, et al. Education and self‐management: a one‐year randomized trial in stable adult asthmatic patients. Journal of Asthma 2002;39:493‐500. - PubMed
Espinosa 1998 {published data only}
-
- Espinosa de los Monteros Garde MJ, Ancochea Bermadez J, Rodriguez Salvanés F, Fuente S, Rodriguez M, Gonzalez Gamarra A. Randomised comparison of quality of life of guided self management and traditional treatments of asthma in Spain. Preliminary communication [Abstract]. European Respiratory Journal. 1998; Vol. 12, issue 26s:26s, P198.
Fernandes 2011 {published data only}
-
- Fernandes L, Mesquita A. Improving asthma control with therapeutic education intervention [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. 2011; Vol. 38:913s [P4997].
Fonseca 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fonseca JA, Costa‐Pereira A, Delgado L, Fernandes L, Castel‐Branco MG. Asthma patients are willing to use mobile and web technologies to support self‐management. Allergy 2006;61(3):389‐90. - PubMed
Ford 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ford ME, Edwards G, Rodriguez JL, Gibson RC, Tilley BC. An empowerment‐centered, church‐based asthma education program for African American adults. Health & Social Work 1996;21(1):70‐5. - PubMed
Ford 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ford ME, Havstad SL, Tilley BC, Boulton MB. Health outcomes among African American and Caucasian adults following a randomized trial of an asthma education program. Ethnicity & Health 1997;2:329‐39. - PubMed
Gaga 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gaga M, Karokis A, Papageorgiou M, Gourgoulianis K, Loukides S, Yourgioti G, et al. Are written action plans or physicians' instructions more effective for asthmatic patients regularly followed by pulmonary specialists? [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society 100th International Conference. 2004:B45 poster A47.
Gallefoss 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gallefoss F, Bakke PS. Cost‐effectiveness of self‐management in asthmatics ‐ a one‐year follow‐up randomised, controlled trial. Annual Thoracic Society 97th International Conference; San Francisco, CA, May 18‐23. 2001.
Goeman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Goeman D, Jenkins C, Crane M, Paul E, Douglass J. Educational intervention for older people with asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Patient Education and Counseling 2013;93:586‐95. - PubMed
GRASSIC 1994 {published data only}
Haniotou 2012 {published data only}
-
- Haniotou A, Grammatopoulou E, Koutsouki D. The effect of a self‐management program on quality of life in patients with stable asthma: a pilot study [Abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2012; Vol. 185:A2878.
Ignacio 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ignacio Garcia JM, Gonzalez Santos P. Asthma self‐management education program by home monitoring of peak expiratory flow. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1995;151:353‐9. - PubMed
Janson 2009 {published data only}
Kelso 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kelso TM, Abou‐Shala N, Heilker GM, Arheart KL, Portner TS, Self TH. Comprehensive long‐term management program for asthma: effect on outcomes in adult African‐Americans. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1996;311(6):272‐80. - PubMed
Kemple 2002a {published data only}
-
- Kemple T. Prompting better asthma self‐management:results from a randomised controlled trial [Abstract]. International Primary Care Respiratory Group Congress. 2002:61.
Kim 2016 {published data only}
Kokubu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kokubu F, Nakajima S, Ito K, Makino S, Kitamura S, Fukuchi Y, et al. Hospitalization reduction by an asthma tele‐medicine system. Allergy [Arerugi] 2000;49(1):19‐31. - PubMed
Kotses 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kotses H, Stout C, McConnaughty K, Winder JA, Creer TL. Evaluation of individualized asthma self‐management programs. Journal of Asthma 1996;33(2):113‐8. - PubMed
Lahdensuo 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lahdensuo A, Haahtela T, Herrala J, Kava T, Kiviranta K, Kuusisto P, et al. PEF‐guided use of an inhaled corticosteroid is successful. The Finnish asthma self‐management study [abstract]. European Respiratory Journal. 1994; Vol. 7:142s.
Lahdensuo 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lahdensuo A, Haahtela T, Herrala J, Kava T, Kiviranta K, Kuusisto P, et al. PEF‐guided use of an inhaled corticosteroid is successful. The Finnish asthma self‐management study [abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 1994;7:142s.
Levy 1995 {published data only}
-
- Levy ML, Robb M, Allen J, Doherty C, Bland JM, Winter RJ. A randomized controlled evaluation of specialist nurse education following accident and emergency department attendance for acute asthma. Respiratory Medicine 2000;94:900‐8. - PubMed
-
- Levy ML, Robb M, Allen J, Doherty C, Bland M, Winter RJD. Guided self‐management reduces morbidity, time off work and consultations for uncontrolled asthma in adults [abstract]. Annual Congress of the European Respiratory Society. 1995; Vol. 8:318s.
Lincicome 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lincicome V, Lozano P, Jones C, Bryant JE, Finkelstein J, Shulruff R, et al. The nurse‐patient collaboration: experiences with a self‐management support intervention for asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2001;107(2):S73.
Magar 2005 {published data only}
-
- Magar Y, Vervloet D, Steenhouwer F, Smaga S, Mechin H, Rocca Serra JP, et al. Assessment of a therapeutic education programme for asthma patients: "un souffle nouveau". Patient Education & Counseling 2005;58:41‐6. - PubMed
McLean 2003 {published data only}
-
- McLean W, Gillis J, Waller R. The BC Community Pharmacy Asthma Study: a study of clinical, economic and holistic outcomes influenced by an asthma care protocol provided by specially trained community pharmacists in British Columbia. Canadian Respiratory Journal [Revue Canadienne de Pneumologie] 2003;10:195‐202. - PubMed
NCT00129662 {published data only}
-
- NCT00129662. Comprehension and Evaluation of a Pictorial Action Plan for Those With Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00129662 2005.
NCT00214669 2005 {published data only}
-
- NCT00214669. Can Education for South Asians With Asthma and Their Clinicians Reduce Unscheduled Care? A Cluster Randomised Trial. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00214669 2005.
NCT01070095 {published data only}
-
- NCT01070095. The Electronic Asthma Action Plan System for Implementation in Primary Care. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01070095 2012.
NCT01079000 2012 {published data only}
-
- NCT01079000. Emergency Department (ED)‐Directed Interventions to Improve Outcomes After Asthma Exacerbations. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01079000 2012.
NCT01282359 {published data only}
-
- NCT01282359. Efficacy of a Minimal Intervention Educational Program in the Asthma Control and Exacerbations Prevention. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01282359 2011.
NCT02046759 {published data only}
-
- NCT01079000. Emergency Department (ED)‐Directed Interventions to Improve Outcomes After Asthma Exacerbations. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01079000 2012.
NCT02091869 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT02091869. A Randomized Trial Examining the Effectiveness of Mobile‐Based Asthma Action Plans vs. Paper Asthma Action Plans. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02091869 2014.
Olivera 2016 {published data only}
-
- Olivera CM, Vianna EO, Bonizio RC, Menezes MB, Ferraz E, Cetlin AA, et al. Asthma self‐management model: randomized controlled trial. Health Education Research 2016;[Epub ahead of print]:[Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Osman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Osman LM, Calder C, Friend JA, Legge JS, Douglas JG. A self management plan increases satisfactoin and reduces morbidity among adult patients one month after discharge. European Respiratory Journal 2001;18:4s.
Parkes 2012 {published data only}
-
- Parkes J, Findlay J, Ward A, Richardson M. Zoned asthma action plan (Zaap) ‐ a self‐assessment tool for patients with asthma [Abstract]. 6th IPCRG World Conference. 2012:Abstract 243.
Patel 2015 {published data only}
-
- Patel AM, Yusin JS. Role of patient education in the management and control of asthma in the adult population. VA Greater Los Angeles Health Care System. 2015; Vol. 135:AB68.
Put 2001 {published data only}
-
- Put C, Bergh O, Lemaigre V, Demedts M, Verleden G. Evaluation of an individualised asthma programme directed at behavioural change. The European Respiratory Journal 2003;21(1):109‐15. - PubMed
-
- Put CL, Verleden G, Bergh O, Demedts M. Evaluation of an individualized asthma program aiming at behavioral change. Annual Thoracic Society 97th International Conference. 2001.
Ross 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ross JA, Clark NM, Baptist A. An asthma self‐management Intervention can improve outcomes for older adults [Abstract]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2012;129:AB142 [539].
Sittipunt 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sittipunt C, Canhanapan K, Kasettratat N. Outcomes of self management educational program for asthmatic patients with a history of severe exacerbation [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2008:A839 [#401].
Steurer‐Stey 2010 {published data only}
-
- Steurer‐Stey C, Storch M, Steffen‐Bargi B, Steurer J, Puhan M, Steffen‐Bürgi B. A general self‐management program improves self‐efficacy but not short‐term adherence with asthma self‐management behavior: a randomized controlled trial [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. 2010:[P3989].
Tousman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tousman S, Zeitz H. Randomized control behavioral trial of adult asthma self‐management program [Abstract]. American Thoracic Society International Conference. 2009:A1087 [Poster #516].
Tuazon 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tuazon JA. Comparison of two adult asthma education programs in enhancing self‐care behaviors and symptom control [abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;161:A54.
-
- Tuazon JA. Two years follow‐up effects of asthma education programs on inhaler technique, health locus of control, self‐efficacy and self‐care behaviours. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A420.
Urek 2005 {published data only}
-
- Urek MC, Tudorić N, Plavec D, Urek R, Koprivc‐Milenović T, Stojić M. Effect of educational programs on asthma control and quality of life in adult asthma patients. Patient Education and Counseling 2005;58(1):47‐54. - PubMed
Wilson‐Pessano 1987 {published data only}
-
- Wilson‐Pessano SR, Scamagas P, Arsham GM, Chardon L, Coss S, German DF, et al. An evaluation of approaches to asthma self‐management education for adults: the AIR/Kaiser‐Permanente Study. Health Education Quarterly 1987;14(3):333‐43. - PubMed
Zairina 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zairina E, Abramson MJ, McDonald CF, Li J, Dharmasiri T, Stewart K, et al. Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of a telehealth program ‐ management of asthma with supportive telehealth of respiratory function in pregnancy (MASTERY). BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2015;15:84. - PMC - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Angelini 2010 {published data only}
-
- Angelini L, Santos DO, Amorim PBS, Carvalho‐Pinto RM, Cukier A, Stelmach R. Impact of education and self‐management program in moderate and severe persistent control asthma [Abstract]. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. 2010:[E5472].
References to ongoing studies
NCT02190617 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT02190617. Guidelines to Practice: Reducing Asthma Health Disparities Through Guideline Implementation (G2P). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02190617 2014.
NCT02424409 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT02424409. Evaluation of the Relapse Rate One Month After Discharge From Emergency Department for Asthmatic Patients Given a Strict Formalized Follow up Protocol. Multicenter, Prospective, Cluster‐randomized. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02424409 2015.
Additional references
Adams 2009
Bauman 2003
-
- Bauman AE, Fardy HJ, Harris PG. Getting it right: why bother with patient‐centred care?. Medical Journal of Australia 2003;179(1):253‐6. - PubMed
Bhogal 2006
BTS/SIGN 2016
-
- British Thoracic Society, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. British guideline on the management of asthma. sign.ac.uk/pdf/SIGN153.pdf (accessed prior to 28 March 2017).
Charlton 1990
D'Souza 1996
-
- D'Souza W, Burgess C, Ayson M, Crane J, Pearce N, Beasley R. Trial of a "credit card" asthma self‐management plan in a high risk group of patients with asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1996;97(5):1085‐92. - PubMed
Douglas 2002
Ducharme 2008
Gibson 1995
-
- Gibson PG, Talbot PL, Toneguzzi RC, Population Medicine Group 91C. Self‐management, autonomy, and quality of life in asthma. Chest 1995;107(4):1003‐8. - PubMed
Gibson 2003
Gibson 2004
GINA 2016
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention, 2016. www.ginasthma.org (accessed 11 January 2017).
Global Asthma Report 2014
-
- The Global Asthma Report 2014. Auckland, New Zealand: Global Asthma Network, 2014. www.globalasthmareport.org/resources/Global_Asthma_Report_2014.pdf (accessed 20 March 2015).
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University. GRADEpro. McMaster University, 2014.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holt 2004
Jenkinson 1988
Khan 2014
-
- Khan R, Maharaj R, Seerattan N, Babwah F. Effectiveness of personalized written asthma action plans in the management of children with partly controlled asthma in Trinidad: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2014;60(1):17‐26. - PubMed
Kristiansen 2012
-
- Kristiansen J, Hetutu E, Manukia M, Jelleyman T. An evaluation of a pictorial asthma medication plan for pacific children. New Zealand Medical Journal 2012;125(1354):42‐50. - PubMed
Lahdensuo 1999
Le Fevre 2002
-
- Lefevre F, Piper M, Weiss K, Mark D, Clark N, Aronson N. Do written action plans improve patient outcomes in asthma? An evidence‐based analysis. Journal of Family Practice 2002;51(10):842‐8. - PubMed
MacGillivray 2014
Marcano Belisario 2013
NICE 2007
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Inhaled corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years. TA131. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta131 (accessed 23 March 2015).
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Quality standard for asthma. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/qs25 (accessed 23 March 2015).
Normansell 2014
NRAD 2014
-
- Royal College of Physicians. Why asthma still kills: the national review of asthma deaths. www.rcplondon.ac.uk/sites/default/files/why‐asthma‐still‐kills‐full‐repo... (accessed 28 August 2014).
Pearce 2016
-
- Pearce G, Parke H, Pinnock H, Epiphaniou E, Bourne CLA, Sheikh A, et al. The PRISMS taxonomy of self‐management support: derivation of a novel taxonomy and initial testing of utility. Journal of Health Service Research Policy 2016;21:73‐82. - PubMed
Peytremann‐Bridevaux 2015
Pinnock 2015
Powell 2002
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ring 2011
-
- Ring N, Jepson R, Hoskins G, Wilson C, Pinnock H, Sheikh A, et al. Understanding what helps or hinders asthma action plan use: a systematic review and synthesis of the qualitative literature. Patient Education and Counselling 2011;85:e131‐43. - PubMed
Sheares 2015a
Tapp 2007
Toelle 2011
Turner 1998
-
- Turner MO, Taylor D, Bennett R, Fitzgerald JM. A randomized trial comparing peak flow and symptom self‐management plans for patients with asthma attending a primary care clinic. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 1998;157:540‐6. - PubMed
Welsh 2011
Zemek 2008
-
- Zemek RL, Bhogal SK, Ducharme FM. Systematic review of randomized controlled trials examining written action plans in children: what is the plan?. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2008;162(2):157‐63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

