1,3-Butadiene-Induced Adenine DNA Adducts Are Genotoxic but Only Weakly Mutagenic When Replicated in Escherichia coli of Various Repair and Replication Backgrounds
- PMID: 28394575
- PMCID: PMC5512570
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00064
1,3-Butadiene-Induced Adenine DNA Adducts Are Genotoxic but Only Weakly Mutagenic When Replicated in Escherichia coli of Various Repair and Replication Backgrounds
Abstract
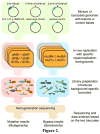
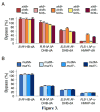
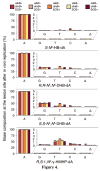
The adverse effects of the human carcinogen 1,3-butadiene (BD) are believed to be mediated by its DNA-reactive metabolites such as 3,4-epoxybut-1-ene (EB) and 1,2,3,4-diepoxybutane (DEB). The specific DNA adducts responsible for toxic and mutagenic effects of BD, however, have yet to be identified. Recent in vitro polymerase bypass studies of BD-induced adenine (BD-dA) adducts show that DEB-induced N6,N6-DHB-dA (DHB = 2,3-dihydroxybutan-1,4-diyl) and 1,N6-γ-HMHP-dA (HMHP = 2-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylpropan-1,3-diyl) adducts block replicative DNA polymerases but are bypassed by human polymerases η and κ, leading to point mutations and deletions. In contrast, EB-induced N6-HB-dA (HB = 2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl) does not block DNA synthesis and is nonmutagenic. In the present study, we employed a newly established in vivo lesion-induced mutagenesis/genotoxicity assay via next-generation sequencing to evaluate the in vivo biological consequences of S-N6-HB-dA, R,R-N6,N6-DHB-dA, S,S-N6,N6-DHB-dA, and R,S-1,N6-γ-HMHP-dA. In addition, the effects of AlkB-mediated direct reversal repair, MutM and MutY catalyzed base excision repair, and DinB translesion synthesis on the BD-dA adducts in bacterial cells were investigated. BD-dA adducts showed the expected inhibition of DNA replication in vivo but were not substantively mutagenic in any of the genetic environments investigated. This result is in contrast with previous in vitro observations and opens the possibility that E. coli repair and bypass systems other than the ones studied here are able to minimize the mutagenic properties of BD-dA adducts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
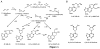
References
-
- Pelz N, Dempster NM, Shore PR. Analysis of low molecular weight hydrocarbons including 1,3-butadiene in engine exhaust gases using an aluminum oxide porous-layer open-tubular fused-silica column. J Chromatogr Sci. 1990;28:230–235. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS. Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:1194–1210. - PubMed
-
- White WC. Butadiene production process overview. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;166:10–14. - PubMed
-
- Melnick RL, Kohn MC. Mechanistic data indicate that 1,3-butadiene is a human carcinogen. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:157–163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

