The acute impact of high-dose lipid-lowering treatment on endothelial progenitor cells in patients with coronary artery disease-The REMEDY-EPC early substudy
- PMID: 28394933
- PMCID: PMC5386268
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172800
The acute impact of high-dose lipid-lowering treatment on endothelial progenitor cells in patients with coronary artery disease-The REMEDY-EPC early substudy
Abstract
Rationale and objective: Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) play a role in vascular repair, while circulating endothelial cells (CECs) are biomarkers of vascular damage and regeneration. Statins may promote EPC/CEC mobilization in the peripheral blood. We evaluated whether pre-procedural exposure to different lipid-lowering drugs (statins±ezetimibe) can acutely increase levels/activity of EPCs/CECs in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD).
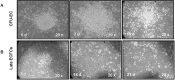
Methods: In a planned sub-analysis of the Rosuvastatin For REduction Of Myocardial DamagE During Coronary AngioplastY (REMEDY) trial, 38 patients with stable CAD on chronic low-dose statin therapy were randomized, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled design, into 4 groups before PCI: i. placebo (n = 11); ii. atorvastatin (80 mg+40 mg, n = 9); iii. rosuvastatin (40 mg twice, n = 9); and iv. rosuvastatin (5 mg) and ezetimibe (10 mg) twice, (n = 9). At baseline and 24 h after treatment-before PCI-, patients underwent blinded analyses of EPCs [colony forming units-endothelial cells (CFU-ECs), endothelial colony-forming cells (ECFCs) and tubulization activity] and CECs in peripheral blood.
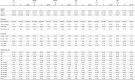
Results: We found no significant treatment effects on parameters investigated such as number of CECs [Median (IQR): i. 0(0), ii. 4.5(27), iii. 1.9(2.3), iv. 1.9(2.3)], CFU-ECs [Median (IQR): i. 27(11), ii. 19(31), iii. 47(36), iv. 30(98)], and ECFCs [Median (IQR): i. 86(84), ii. 7(84), iii. 8/(42.5), iv. 5(2)], as well as tubulization activity [total tubuli (well), Median (IQR): i. 19(7), ii. 5(4), iii. 25(13), iv. 15(24)].
Conclusions: In this study, we found no evidence of acute changes in levels or activity of EPCs and CECs after high-dose lipid-lowering therapy in stable CAD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Perin E, Dohmann H, Borojevic R, Silva S, Sousa A, Mesquita C, et al. Transendocardial, autologous bone marrow cell transplantation for severe, chronic ischemic heart failure. Circulation. 2009;107:2294–302. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275:964–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

