Vitamin D suppresses oxidative stress-induced microparticle release by human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 28395329
- PMCID: PMC6025229
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.142604
Vitamin D suppresses oxidative stress-induced microparticle release by human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
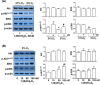
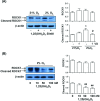
Endothelial microparticle (MP) release was increased in numerous cardiovascular diseases including preeclampsia. Oxidative stress is a potent inducer of endothelial dysfunction. In this study, we aimed to investigate if vitamin D could protect endothelial cells (ECs) from MP release induced by oxidative stress. Endothelial cell (from human umbilical vein) oxidative stress was induced by cultivation of cells under lowered oxygen condition (2%O2) for 48 h and cells cultured under standard condition (21%O2) served as control. 1,25(OH)2D3 was used as bioactive vitamin D. Using annexin-V as a marker of released MP assessed by flow cytometry and cytochrome c reduction assay to measure EC superoxide generation, we found that MP release and superoxide generation were significantly increased when cells were cultured under 2%O2, which could be significantly inhibited by 1,25(OH)2D3. To study the potential mechanisms of 1,25(OH)2D3 protective effects on ECs, EC expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), p-eNOSSer1177, p-eNOSThr495, caveolin-1, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p-ERK, Akt, p-AktSer473, Rho-associated coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK1), and vitamin D receptor were determined. Microparticle expression of eNOS and caveolin-1 were also determined. We found that under lowered oxygen condition, 1,25(OH)2D3 could upregulate EC eNOS, p-eNOSSer1177, and p-AktSer473 expression, but inhibit cleaved ROCK1 expression. The upregulatory and inhibitory effects induced by 1,25(OH)2D3 were dose dependent. Strikingly, we also found that oxidative stress-induced decrease in ratio of eNOS and caveolin-1 expression in MP could be attenuated when 1,25(OH)2D3 was present in culture. These results suggest that upregulation of eNOSSer1177 and AktSer473 phosphorylation and inhibition of ROCK1 cleavage in EC and modulation of eNOS and caveolin-1 expression in MP could be plausible mechanisms of vitamin D protective effects on ECs.
Keywords: Akt; ROCK; eNOS; endothelial cells; microparticles; vitamin D.
© The Authors 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for the Study of Reproduction. All rights reserved. For permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vitamin D Reduces Oxidative Stress-Induced Procaspase-3/ROCK1 Activation and MP Release by Placental Trophoblasts.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jun 1;102(6):2100-2110. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-3753. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28368445 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol ameliorates low shear stress‑induced oxidative stress by suppressing ERK/eNOS‑Thr495 in endothelial cells.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Oct;10(4):1964-72. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2390. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25198200
-
Interleukin-6 inhibits endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase binding to stabilized caveolin-1 in human vascular endothelial cells.J Hypertens. 2010 May;28(5):940-51. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32833992ef. J Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20375905
-
Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress by vitamin D in endothelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Oct;99:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.07.020. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27458123
-
The Role of Vitamin D in Neuroprotection in Multiple Sclerosis: An Update.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):2978. doi: 10.3390/nu15132978. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Exosomes/Microvesicles Derived from Myeloid Dendritic Cells Cultured in the Presence of Calcitriol and Tacalcitol on Acute B-Cell Precursor Cell Lines with MLL Fusion Gene.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 15;11(8):2224. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082224. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35456315 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Improves Nitric Oxide-Dependent Vasodilation in Adipose Tissue Arterioles from Bariatric Surgery Patients.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 18;11(10):2521. doi: 10.3390/nu11102521. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31635396 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Suggesting a Relationship between Vitamin D and Erectile Dysfunction: An Overview.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 1;13(6):930. doi: 10.3390/biom13060930. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating endothelial dysfunction with vitamin D in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Sep 25;19(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-1042-y. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30253741 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in microparticle profiles by vitamin D receptor activation in chronic kidney disease - a randomized trial.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Aug 1;20(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1445-4. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31370809 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dignat-George F, Boulanger CM. The many faces of endothelial microparticles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011; 31:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Mezentsev A, Merks RM, O’Riordan E, Chen J, Mendelev N, Goligorsky MS, Brodsky SV. Endothelial microparticles affect angiogenesis in vitro: role of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2005; 289:H1106–H1114. - PubMed
-
- Amabile N, Guérin AP, Leroyer A, Mallat Z, Nguyen C, Boddaert J, London GM, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM. Circulating endothelial microparticles are associated with vascular dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16:3381–3388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

