The WW domain of the scaffolding protein IQGAP1 is neither necessary nor sufficient for binding to the MAPKs ERK1 and ERK2
- PMID: 28396345
- PMCID: PMC5448102
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.767087
The WW domain of the scaffolding protein IQGAP1 is neither necessary nor sufficient for binding to the MAPKs ERK1 and ERK2
Abstract
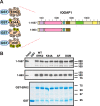
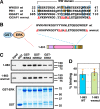
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) scaffold proteins, such as IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 (IQGAP1), are promising targets for novel therapies against cancer and other diseases. Such approaches require accurate information about which domains on the scaffold protein bind to the kinases in the MAPK cascade. Results from previous studies have suggested that the WW domain of IQGAP1 binds to the cancer-associated MAPKs ERK1 and ERK2, and that this domain might thus offer a new tool to selectively inhibit MAPK activation in cancer cells. The goal of this work was therefore to critically evaluate which IQGAP1 domains bind to ERK1/2. Here, using quantitative in vitro binding assays, we show that the IQ domain of IQGAP1 is both necessary and sufficient for binding to ERK1 and ERK2, as well as to the MAPK kinases MEK1 and MEK2. Furthermore, we show that the WW domain is not required for ERK-IQGAP1 binding, and contributes little or no binding energy to this interaction, challenging previous models of how WW-based peptides might inhibit tumorigenesis. Finally, we show that the ERK2-IQGAP1 interaction does not require ERK2 phosphorylation or catalytic activity and does not involve known docking recruitment sites on ERK2, and we obtain an estimate of the dissociation constant (Kd ) for this interaction of 8 μm These results prompt a re-evaluation of published findings and a refined model of IQGAP scaffolding.
Keywords: IQGAP1; cancer; cell signaling; extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); protein complex; protein kinase; protein-protein interaction; scaffold protein.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
-
- Dhillon A. S., Hagan S., Rath O., and Kolch W. (2007) MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26, 3279–3290 - PubMed
-
- Lawrence M. C., Jivan A., Shao C., Duan L., Goad D., Zaganjor E., Osborne J., McGlynn K., Stippec S., Earnest S., Chen W., and Cobb M. H. (2008) The roles of MAPKs in disease. Cell Res. 18, 436–442 - PubMed
-
- Caunt C. J., Sale M. J., Smith P. D., and Cook S. J. (2015) MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road. Nat. Rev. Cancer 15, 577–592 - PubMed
-
- Lito P., Rosen N., and Solit D. B. (2013) Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat. Med. 19, 1401–1409 - PubMed
-
- Dhanasekaran D. N., Kashef K., Lee C. M., Xu H., and Reddy E. P. (2007) Scaffold proteins of MAP-kinase modules. Oncogene 26, 3185–3202 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

