Common polymorphisms of the hOGG1, APE1 and XRCC1 genes correlate with the susceptibility and clinicopathological features of primary angle-closure glaucoma
- PMID: 28396513
- PMCID: PMC5477560
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160644
Common polymorphisms of the hOGG1, APE1 and XRCC1 genes correlate with the susceptibility and clinicopathological features of primary angle-closure glaucoma
Abstract
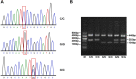
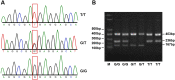
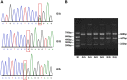
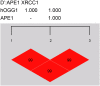
The present case study aims to elucidate the correlation between the human 8-hydroxyguanineglycosylase (hOGG1), APE1 and X-ray repair cross-complementing gene 1 (XRCC1) gene polymorphisms to the susceptibility and clinicopathological features of primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG) in a Chinese Han population. Blood samples were obtained from 258 PACG patients (case group) and 272 healthy volunteers (control group). PCR with sequence-specific primer (PCR-SSP) was used to determine the allele frequencies and genotype distributions of the hOGG1, APE1 and XRCC1 genes. The risk factors of PACG were determined using logistic regression analysis. The results indicated that hOGG1 Ser326Cys, APE1 Asp148Glu and XRCC1 Arg399Gln polymorphisms were correlated with the risk of PACG. Furthermore, there were thicker corneas, higher intraocular pressure (IOP) and a shorter axial length in patients carrying the mutant genotypes of hOGG1 Ser326Cys (Ser/Cys + Cys/Cys), APE1 Asp148Glu (Asp/Glu + Glu/Glu) and XRCC1 Arg399Gln (Arg/Gln + Glu/Glu) than those carrying the corresponding wild-type genotypes. According to the logistic regression analysis, Asp148Glu and Arg399Gln polymorphisms, a short axial length and high IOP are major risk factors for PACG. These findings reveal that hOGG1 Ser326Cys, APE1 Asp148Glu and XRCC1 Arg399Gln polymorphisms are correlated with the risk and clinicopathological features of PACG in a Chinese Han population.
Keywords: APE1; Clinicopathological features; Polymorphism; Primary angle-closure glaucoma; Susceptibility; XRCC1; hOGG1.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APE1 polymorphisms are associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility in Chinese Hans.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 14;20(26):8700-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8700. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25024628 Free PMC article.
-
Association of APE1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms with colorectal cancer risk in a Turkish population.Curr Med Res Opin. 2011 Jul;27(7):1295-302. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.573544. Epub 2011 May 12. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011. PMID: 21561390
-
Association of DNA base-excision repair XRCC1, OGG1 and APE1 gene polymorphisms with nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility in a Chinese population.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5145-51. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.9.5145. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24175791
-
Association between OGG1 Ser326Cys and APEX1 Asp148Glu polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Jun 3;9:108. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-108. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24893568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Mar 4;19(1):20240913. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0913. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. Retraction in: Open Med (Wars). 2024 Jun 12;19(1):20241000. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1000. PMID: 38463515 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Asian Race and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: Where Do We Stand?J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 28;11(9):2486. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092486. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

