Evaluation of GRCh38 and de novo haploid genome assemblies demonstrates the enduring quality of the reference assembly
- PMID: 28396521
- PMCID: PMC5411779
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.213611.116
Evaluation of GRCh38 and de novo haploid genome assemblies demonstrates the enduring quality of the reference assembly
Abstract
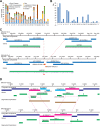
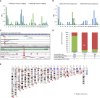
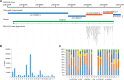
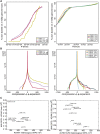
The human reference genome assembly plays a central role in nearly all aspects of today's basic and clinical research. GRCh38 is the first coordinate-changing assembly update since 2009; it reflects the resolution of roughly 1000 issues and encompasses modifications ranging from thousands of single base changes to megabase-scale path reorganizations, gap closures, and localization of previously orphaned sequences. We developed a new approach to sequence generation for targeted base updates and used data from new genome mapping technologies and single haplotype resources to identify and resolve larger assembly issues. For the first time, the reference assembly contains sequence-based representations for the centromeres. We also expanded the number of alternate loci to create a reference that provides a more robust representation of human population variation. We demonstrate that the updates render the reference an improved annotation substrate, alter read alignments in unchanged regions, and impact variant interpretation at clinically relevant loci. We additionally evaluated a collection of new de novo long-read haploid assemblies and conclude that although the new assemblies compare favorably to the reference with respect to continuity, error rate, and gene completeness, the reference still provides the best representation for complex genomic regions and coding sequences. We assert that the collected updates in GRCh38 make the newer assembly a more robust substrate for comprehensive analyses that will promote our understanding of human biology and advance our efforts to improve health.
© 2017 Schneider et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
