Click Chemistry-Facilitated Structural Diversification of Nitrothiazoles, Nitrofurans, and Nitropyrroles Enhances Antimicrobial Activity against Giardia lamblia
- PMID: 28396548
- PMCID: PMC5444119
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02397-16
Click Chemistry-Facilitated Structural Diversification of Nitrothiazoles, Nitrofurans, and Nitropyrroles Enhances Antimicrobial Activity against Giardia lamblia
Abstract
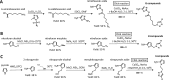
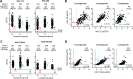
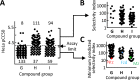
Giardia lamblia is an important and ubiquitous cause of diarrheal disease. The primary agents in the treatment of giardiasis are nitroheterocyclic drugs, particularly the imidazoles metronidazole and tinidazole and the thiazole nitazoxanide. Although these drugs are generally effective, treatment failures occur in up to 20% of cases, and resistance has been demonstrated in vivo and in vitro Prior work had suggested that side chain modifications of the imidazole core can lead to new effective 5-nitroimidazole drugs that can combat nitro drug resistance, but the full potential of nitroheterocycles other than imidazole to yield effective new antigiardial agents has not been explored. Here, we generated derivatives of two clinically utilized nitroheterocycles, nitrothiazole and nitrofuran, as well as a third heterocycle, nitropyrrole, which is related to nitroimidazole but has not been systematically investigated as an antimicrobial drug scaffold. Click chemistry was employed to synthesize 442 novel nitroheterocyclic compounds with extensive side chain modifications. Screening of this library against representative G. lamblia strains showed a wide spectrum of in vitro activities, with many of the compounds exhibiting superior activity relative to reference drugs and several showing >100-fold increase in potency and the ability to overcome existing forms of metronidazole resistance. The majority of new compounds displayed no cytotoxicity against human cells, and several compounds were orally active against murine giardiasis in vivo These findings provide additional impetus for the systematic development of nitroheterocyclic compounds with nonimidazole cores as alternative and improved agents for the treatment of giardiasis and potentially other infectious agents.
Keywords: antimicrobial agents; drug screening.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
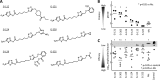
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

