Riboswitch diversity and distribution
- PMID: 28396576
- PMCID: PMC5473149
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.061234.117
Riboswitch diversity and distribution
Abstract
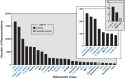
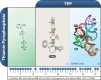
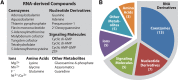
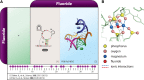
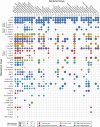
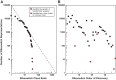
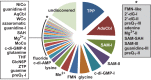
Riboswitches are commonly used by bacteria to detect a variety of metabolites and ions to regulate gene expression. To date, nearly 40 different classes of riboswitches have been discovered, experimentally validated, and modeled at atomic resolution in complex with their cognate ligands. The research findings produced since the first riboswitch validation reports in 2002 reveal that these noncoding RNA domains exploit many different structural features to create binding pockets that are extremely selective for their target ligands. Some riboswitch classes are very common and are present in bacteria from nearly all lineages, whereas others are exceedingly rare and appear in only a few species whose DNA has been sequenced. Presented herein are the consensus sequences, structural models, and phylogenetic distributions for all validated riboswitch classes. Based on our findings, we predict that there are potentially many thousands of distinct bacterial riboswitch classes remaining to be discovered, but that the rarity of individual undiscovered classes will make it increasingly difficult to find additional examples of this RNA-based sensory and gene control mechanism.
Keywords: RNA World; aptamer; coenzyme; ligand; noncoding RNA.
© 2017 McCown et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
References
-
- Ames TD, Breaker RR. 2010. Bacterial riboswitch discovery and analysis. In The chemical biology of nucleic acids (ed. Mayer G). Wiley, Chichester, UK.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
