Down-regulation of miR-214 reverses erlotinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer through up-regulating LHX6 expression
- PMID: 28396596
- PMCID: PMC5429707
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00901-6
Down-regulation of miR-214 reverses erlotinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer through up-regulating LHX6 expression
Abstract
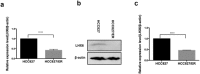
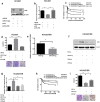
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are standard treatments for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. However, acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs is widely detected across the world, and the exact mechanisms have not been fully demonstrated until now. This study aimed to examine the role of miR-214 in the acquired resistance to erlotinib in NSCLC, and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. qRT-PCR assay detected higher miR-214 expression in the plasma of NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance than prior to EGFR-TKI therapy, and in the generated erlotinib-resistant HCC827 (HCC827/ER) cells than in HCC827 cells. Bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay indentified LHX6 as a direct target gene of miR-214, and LHX6 expression was detected to be down-regulated in erlotinib-resistant HCC827 cells. Transwell invasion assay revealed that overexpressing LHX6 reversed the increase in the invasive ability of HCC827 cells induced by miR-214 overexpression, and the CRISPR-Cas9 system-mediated LHX6 knockdown reversed the reduction in the invasion of erlotinib-resistant HCC827 cells caused by miR-214 down-regulation. The results of the present study demonstrate that down-regulation of miR-214 may reverse acquired resistance to erlotinib in NSCLC through mediating its direct target gene LHX6 expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

