Cinnamon Polyphenol Extract Inhibits Hyperlipidemia and Inflammation by Modulation of Transcription Factors in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats
- PMID: 28396714
- PMCID: PMC5370473
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1583098
Cinnamon Polyphenol Extract Inhibits Hyperlipidemia and Inflammation by Modulation of Transcription Factors in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats
Abstract
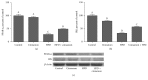
We evaluated the effects of cinnamon polyphenol extract on hepatic transcription factors expressions including SREBP-1c and LXR-α in rats fed high fat diet (HFD). Twenty-eight Wistar rats were allocated into four groups: (i) normal control: animals fed with normal chow; (ii) cinnamon: animals supplemented with cinnamon polyphenol; (iii) HFD: animals fed a high-fat diet; and (iv) HFD + cinnamon: animals fed a high-fat diet and treated with cinnamon polyphenol. Obesity was linked to hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress as imitated by elevated serum glucose, lipid profile, and serum and liver malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations. Cinnamon polyphenol decreased body weight, visceral fat, liver weight and serum glucose and insulin concentrations, liver antioxidant enzymes, and lipid profile (P < 0.05) and reduced serum and liver MDA concentration compared to HFD rats (P < 0.05). Cinnamon polyphenol also suppressed the hepatic SREBP-1c, LXR-α, ACLY, FAS, and NF-κB p65 expressions and enhanced the PPAR-α, IRS-1, Nrf2, and HO-1 expressions in the HFD rat livers (P < 0.05). In conclusion, cinnamon polyphenol reduces the hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress through activating transcription factors and antioxidative defense signaling pathway in HFD rat liver.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cinnamon could improve hepatic steatosis caused by a high-fat diet via enhancing hepatic beta-oxidation and inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis, oxidative damage, and inflammation in male rats.J Food Biochem. 2022 Jun;46(6):e14077. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14077. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35246859
-
Germacrone Attenuates Hyperlipidemia and Improves Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6J Mice.J Med Food. 2017 Jan;20(1):46-55. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.3811. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28098516
-
β-Cryptoxanthin ameliorates metabolic risk factors by regulating NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways in insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet in rodents.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Sep;107(Pt A):270-279. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28689061
-
Cinnamon improves insulin sensitivity and alters the body composition in an animal model of the metabolic syndrome.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Sep 1;501(1):158-61. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.05.032. Epub 2010 May 31. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20515642 Review.
-
Polyphenols and Glycemic Control.Nutrients. 2016 Jan 5;8(1):17. doi: 10.3390/nu8010017. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 26742071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of Redox Equilibrium in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis-Impact of Antioxidant-Rich Diet.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 20;12(6):1841. doi: 10.3390/nu12061841. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32575706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of changes in cytochrome P450 2C19 activity in type 2 diabetic rats before and after treatment, by using isolated perfused liver model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 May;23(5):629-635. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.40836.9642. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32742601 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamon: an aromatic condiment applicable to chronic kidney disease.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2023 Jan;42(1):4-26. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.22.111. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 36747357 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Cinnamaldehyde Enhances Growth Performance, Digestion, Immunity, and Lipid Metabolism in Juvenile Fat Greenling (Hexagrammos otakii).Aquac Nutr. 2022 Nov 2;2022:2132754. doi: 10.1155/2022/2132754. eCollection 2022. Aquac Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36860471 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulation of cinnamon oil in whey protein counteracts the disturbances in biochemical parameters, gene expression, and histological picture of the liver and pancreas of diabetic rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jan;27(3):2829-2843. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07164-w. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31834580
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

