Current trends in European renal epidemiology
- PMID: 28396733
- PMCID: PMC5381210
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfw150
Current trends in European renal epidemiology
Abstract
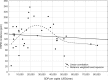
The incidence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) continues to vary substantially between the countries in Europe that contribute data to the ERA-EDTA Registry. Differences can be attributed to socioeconomic factors and prophylaxis programs for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and may also express real differences in CKD incidence. Recently, age-adjusted ESRD incidence has begun to fall in many countries, probably related to improved prophylaxis. However, absolute rates may increase, partly due to socioeconomic advances in countries with a low gross domestic product and partly due to continuing increases in the proportion of elderly patients. Prevalence rates are expected to continue to increase, mainly due to increases in relative transplant prevalence, improved graft survival times and continuing improvements in both dialysis and transplant patient survival. Overall treatment results continue to improve.
Keywords: Europe; dialysis; epidemiology; transplantation.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

