Rab11-FIP1 phosphorylation by MARK2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells
- PMID: 28396819
- PMCID: PMC5383218
- DOI: 10.1080/21592799.2016.1271498
Rab11-FIP1 phosphorylation by MARK2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells
Abstract
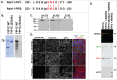
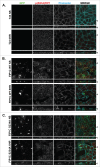
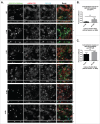
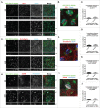
MARK2/Par1b/EMK1, a serine/threonine kinase, is required for correct apical/basolateral membrane polarization in epithelial cells. However, the specific substrates mediating MARK2 action are less well understood. We have now found that MARK2 phosphorylates Rab11-FIP1B/C at serine 234 in a consensus site similar to that previously identified in Rab11-FIP2. In MDCK cells undergoing repolarization after a calcium switch, antibodies specific for pS234-Rab11-FIP1 or pS227-Rab11-FIP2 demonstrate that the spatial and temporal activation of Rab11-FIP1 phosphorylation is distinct from that for Rab11-FIP2. Phosphorylation of Rab11-FIP1 persists through calcium switch and remains high after polarity has been reestablished whereas FIP2 phosphorylation is highest early in reestablishment of polarity but significantly reduced once polarity has been re-established. MARK2 colocalized with FIP1B/C/D and p(S234)-FIP1 in vivo. Overexpression of GFP-Rab11-FIP1C wildtype or non-phosphorylatable GFP-Rab11-FIP1C(S234A) induced two significant phenotypes following calcium switch. Overexpression of FIP1C wildtype and FIP1C(S234A) caused a psuedo-stratification of cells in early time points following calcium switch. At later time points most prominently observed in cells expressing FIP1C(S234A) a significant lateral lumen phenotype was observed, where F-actin-rich lateral lumens appeared demarcated by a ring of ZO1 and also containing ezrin, syntaxin 3 and podocalyxin. In contrast, p120 and E-Cadherin were excluded from the new apical surface at the lateral lumens and now localized to the new lateral surface oriented toward the media. GFP-FIP1C(S234A) localized to membranes deep to the lateral lumens, and immunostaining demonstrated the reorientation of the centrosome and the Golgi apparatus toward the lateral lumen. These results suggest that both Rab11-FIP1B/C and Rab11-FIP2 serve as critical substrates mediating aspects of MARK2 regulation of epithelial polarity.
Keywords: MARK2; Rab11-FIP1; epithelial cell polarity; lateral lumen.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MARK2/EMK1/Par-1Balpha phosphorylation of Rab11-family interacting protein 2 is necessary for the timely establishment of polarity in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Aug;17(8):3625-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0736. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16775013 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of phosphorylated Rab11-FIP2 with Eps15 regulates apical junction composition.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Apr 15;28(8):1088-1100. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0214. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28228550 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Rab11-FIP2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jun;23(12):2302-18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0681. Epub 2012 May 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22553350 Free PMC article.
-
The Rab11-FIP1/RCP gene codes for multiple protein transcripts related to the plasma membrane recycling system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Jun;1759(6):281-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16920206
-
Rab11-family interacting proteins define spatially and temporally distinct regions within the dynamic Rab11a-dependent recycling system.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Mar;24(5):643-58. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-09-0659. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23283983 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rab11-FIP1 and Rab11-FIP5 Regulate pIgR/pIgA Transcytosis through TRIM21-Mediated Polyubiquitination.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10466. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910466. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638806 Free PMC article.
-
PKA-independent vasopressin signaling in renal collecting duct.FASEB J. 2020 May;34(5):6129-6146. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902982R. Epub 2020 Mar 26. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32219907 Free PMC article.
-
IRSp53 controls plasma membrane shape and polarized transport at the nascent lumen in epithelial tubules.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 14;11(1):3516. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17091-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32665580 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11FIP1-deficient mice develop spontaneous inflammation and show increased susceptibility to colon damage.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):G239-G254. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00042.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35819177 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of MARK2, CCDC71, GATA2, and KLRC3 as candidate diagnostic genes and potential therapeutic targets for repeated implantation failure with antiphospholipid syndrome by integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 13;14:1126103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126103. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37901230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo S, Kemphues KJ. par-1, a gene required for establishing polarity in C. elegans embryos, encodes a putative Ser/Thr kinase that is asymmetrically distributed. Cell 1995; 81:611-20. - PubMed
-
- Elbert M, Rossi G, Brennwald P. The yeast par-1 homologs kin1 and kin2 show genetic and physical interactions with components of the exocytic machinery. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16:532-49; PMID:15563607; http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0549 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shulman JM, Benton R, St Johnston D. The Drosophila homolog of C. elegans PAR-1 organizes the oocyte cytoskeleton and directs oskar mRNA localization to the posterior pole. Cell 2000; 101:377-88. - PubMed
-
- Drewes G, Ebneth A, Preuss U, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E. MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption. Cell 1997; 89:297-308; PMID:9108484; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80208-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cohen D, Brennwald PJ, Rodriguez-Boulan E, Musch A. Mammalian PAR-1 determines epithelial lumen polarity by organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol 2004; 164:717-27; PMID:14981097; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200308104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
