Optimization of the GBMV2 implicit solvent force field for accurate simulation of protein conformational equilibria
- PMID: 28397268
- PMCID: PMC5407932
- DOI: 10.1002/jcc.24734
Optimization of the GBMV2 implicit solvent force field for accurate simulation of protein conformational equilibria
Abstract
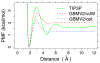
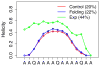
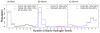
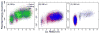
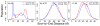
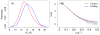
Accurate treatment of solvent environment is critical for reliable simulations of protein conformational equilibria. Implicit treatment of solvation, such as using the generalized Born (GB) class of models arguably provides an optimal balance between computational efficiency and physical accuracy. Yet, GB models are frequently plagued by a tendency to generate overly compact structures. The physical origins of this drawback are relatively well understood, and the key to a balanced implicit solvent protein force field is careful optimization of physical parameters to achieve a sufficient level of cancellation of errors. The latter has been hampered by the difficulty of generating converged conformational ensembles of non-trivial model proteins using the popular replica exchange sampling technique. Here, we leverage improved sampling efficiency of a newly developed multi-scale enhanced sampling technique to re-optimize the generalized-Born with molecular volume (GBMV2) implicit solvent model with the CHARMM36 protein force field. Recursive optimization of key GBMV2 parameters (such as input radii) and protein torsion profiles (via the CMAP torsion cross terms) has led to a more balanced GBMV2 protein force field that recapitulates the structures and stabilities of both helical and β-hairpin model peptides. Importantly, this force field appears to be free of the over-compaction bias, and can generate structural ensembles of several intrinsically disordered proteins of various lengths that seem highly consistent with available experimental data. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: continuum electrostatics; enhanced sampling; generalized Born; intrinsically disordered proteins; nonpolar solvation; protein folding.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
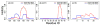
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of generalized born models: Born radii and peptide folding.J Phys Chem B. 2005 Feb 24;109(7):3008-22. doi: 10.1021/jp046307s. J Phys Chem B. 2005. PMID: 16851315
-
Free energy landscape of protein folding in water: explicit vs. implicit solvent.Proteins. 2003 Nov 1;53(2):148-61. doi: 10.1002/prot.10483. Proteins. 2003. PMID: 14517967
-
Balancing solvation and intramolecular interactions: toward a consistent generalized Born force field.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Mar 22;128(11):3728-36. doi: 10.1021/ja057216r. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 16536547 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit modeling of nonpolar solvation for simulating protein folding and conformational transitions.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2008 Jan 28;10(4):471-81. doi: 10.1039/b714141f. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2008. PMID: 18183310 Review.
-
Recent advances in implicit solvent-based methods for biomolecular simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Apr;18(2):140-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.01.003. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18304802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer-Associated Mutations Perturb the Disordered Ensemble and Interactions of the Intrinsically Disordered p53 Transactivation Domain.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 23;433(15):167048. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167048. Epub 2021 May 11. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33984364 Free PMC article.
-
Exact Analytical Algorithm for the Solvent-Accessible Surface Area and Derivatives in Implicit Solvent Molecular Simulations on GPUs.J Chem Theory Comput. 2024 Jun 11;20(11):4456-4468. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c01366. Epub 2024 May 23. J Chem Theory Comput. 2024. PMID: 38780181 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting Coil-to-Globule Transitions to Full Phase Diagrams for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Biophys J. 2020 Jul 21;119(2):402-418. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.06.014. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32619404 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Computational Protocols Addressing Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Biomolecules. 2019 Apr 11;9(4):146. doi: 10.3390/biom9040146. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30979035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations reveal self-association sites in M-crystallin caused by mutations provide insights of cataract.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 2;11(1):23270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02728-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34857812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Best RB, Zhu X, Shim J, Lopes PEM, Mittal J, Feig M, Mackerell AD., Jr Optimization of the Additive CHARMM All-Atom Protein Force Field Targeting Improved Sampling of the Backbone ϕ, ψ and Side-Chain χ 1and χ 2Dihedral Angles. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 2012;8(9):3257–3273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindorff-Larsen K, Piana S, Dror RO, Shaw DE. How fast-folding proteins fold. Science. 2011;334(6055):517–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

