Time course of global gene expression alterations in Candida albicans during infection of HeLa cells
- PMID: 28397609
- PMCID: PMC5474105
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2017.1667
Time course of global gene expression alterations in Candida albicans during infection of HeLa cells
Abstract
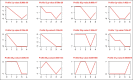
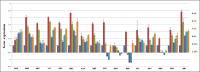
Candida albicans (C. albicans) is an opportunistic fungus that quickly adapts to various microniches. It causes candidiasis, a common fungal infection for which the pathogenic mechanism has not been elucidated yet. To explore the pathogenic mechanism of candidiasis we used several methods, including microscopic observation of morphological changes of HeLa cells and fungus, analysis of differentially expressed genes using gene chips, and a series of biological and bioinformatic analyses to explore genes that are possibly involved in the pathogenesis of C. albicans. During the C. albicans infection, significant morphological changes of the fungus were observed, and the HeLa cells were gradually destroyed. The gene chip experiments showed upregulated expression of 120 genes and downregulated expression of 178 genes. Further analysis showed that some genes may play an important role in the pathogenesis of C. albicans. Overall, morphological variation and adaptive gene expression within a particular microniche may exert important effects during C. albicans infections.
Figures







References
-
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369(9577):1961–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60917-9. - PubMed
-
- Sobel JD. Management of patients with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. Drugs. 2003;63(11):1059–66. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200363110-00002. - PubMed
-
- Sudbery P, Gow N, Berman J. The distinct morphogenic states of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 2004;12(7):317–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2004.05.008. - PubMed
-
- Kabir MA, Hussain MA. Human fungal pathogen Candida albicans in the postgenomic era: An overview. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;7(1):121–34. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.7.1.121. - PubMed
-
- Jones T, Federspiel NA, Chibana H, Dungan J, Kalman S, Magee BB, et al. The diploid genome sequence of Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(19):7329–34. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401648101. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

