Engineering of a synthetic quadrastable gene network to approach Waddington landscape and cell fate determination
- PMID: 28397688
- PMCID: PMC5388541
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.23702
Engineering of a synthetic quadrastable gene network to approach Waddington landscape and cell fate determination
Abstract
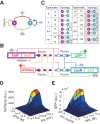
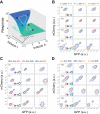
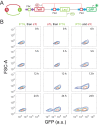
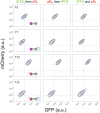
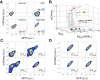
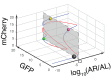
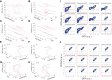
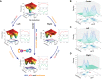
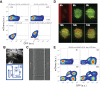
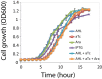
The process of cell fate determination has been depicted intuitively as cells travelling and resting on a rugged landscape, which has been probed by various theoretical studies. However, few studies have experimentally demonstrated how underlying gene regulatory networks shape the landscape and hence orchestrate cellular decision-making in the presence of both signal and noise. Here we tested different topologies and verified a synthetic gene circuit with mutual inhibition and auto-activations to be quadrastable, which enables direct study of quadruple cell fate determination on an engineered landscape. We show that cells indeed gravitate towards local minima and signal inductions dictate cell fates through modulating the shape of the multistable landscape. Experiments, guided by model predictions, reveal that sequential inductions generate distinct cell fates by changing landscape in sequence and hence navigating cells to different final states. This work provides a synthetic biology framework to approach cell fate determination and suggests a landscape-based explanation of fixed induction sequences for targeted differentiation.
Keywords: E. coli; Waddington landscape; cell fate programming; computational biology; quadrastability; sequential induction; synthetic gene network; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators.Elife. 2015 Oct 5;4:e09771. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09771. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26430766 Free PMC article.
-
Decoupling Resource-Coupled Gene Expression in Living Cells.ACS Synth Biol. 2017 Aug 18;6(8):1596-1604. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00119. Epub 2017 May 4. ACS Synth Biol. 2017. PMID: 28459541
-
SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY. Emergent genetic oscillations in a synthetic microbial consortium.Science. 2015 Aug 28;349(6251):986-9. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa3794. Science. 2015. PMID: 26315440 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering molecular circuits using synthetic biology in mammalian cells.Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2012;3:209-34. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-061010-114145. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2012. PMID: 22468602 Review.
-
In silico implementation of synthetic gene networks.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;813:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-412-4_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083733 Review.
Cited by
-
A landscape view on the interplay between EMT and cancer metastasis.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2018 Aug 23;4:34. doi: 10.1038/s41540-018-0068-x. eCollection 2018. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 30155271 Free PMC article.
-
Maximum Caliber Can Build and Infer Models of Oscillation in a Three-Gene Feedback Network.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Jan 17;123(2):343-355. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b07465. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 30507199 Free PMC article.
-
A multiscale model of epigenetic heterogeneity-driven cell fate decision-making.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Apr 30;15(4):e1006592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006592. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31039148 Free PMC article.
-
Simple Rho GTPase Dynamics Generate a Complex Regulatory Landscape Associated with Cell Shape.Biophys J. 2020 Mar 24;118(6):1438-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.01.035. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32084329 Free PMC article.
-
Modularized Design and Construction of Tunable Microbial Consortia with Flexible Topologies.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Jan 19;13(1):183-194. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00420. Epub 2024 Jan 2. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 38166159 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

