Screening, Purification and Characterization of Anionic Antimicrobial Proteins from Foeniculum Vulgare
- PMID: 28397764
- PMCID: PMC6154099
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22040602
Screening, Purification and Characterization of Anionic Antimicrobial Proteins from Foeniculum Vulgare
Abstract
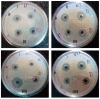
Foeniculum vulgare Mill., commonly called fennel, is a medicinal plant belonging to the Umbelliferae (Apiaceae) family, and is used in traditional medicine. Antibacterial peptides were isolated using sodium phosphate citrate buffer and, for extraction, cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) buffer with pH 6, have been employed and antimicrobial activity tested against four reference strains. The extracted protein was subjected to 3 kDa dialysis and separation was carried out by DEAE-ion exchange chromatography and further proteins were identified by 2D gel electrophoresis. The results of Foeniculum vulgare elutes obtained from DEAE-ion exchange chromatography were tested for antibacterial activity. Elute 3 shows the highest antibacterial activity on Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a diameter of a zone of inhibition of 16 mm and IC50 value 25.02 (mcg/mL). Based on the findings of the wide usage in treatment of various ailments and day-to-day life, Foeniculum vulgare seeds were used in the present research and have shown promising antibacterial effects, which requires further proteomic research to authenticate the role of the anticipated proteins.
Keywords: Foeniculum vulgare; antimicrobial proteins; ion exchange chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial constituents of Foeniculum vulgare.Arch Pharm Res. 2002 Apr;25(2):154-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02976556. Arch Pharm Res. 2002. PMID: 12009028
-
Purification and MIC analysis of antimicrobial proteins from Cucumis sativus L. seeds.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Apr 3;18(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2176-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29615020 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and phytochemical screening of Anethum graveolens, Foeniculum vulgare and Trachyspermum ammi.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009 Aug 6;9:30. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-30. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009. PMID: 19656417 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Composition, functional properties, potential health benefits, and safety.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(20):6924-6941. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2176817. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36803269 Review.
-
Foeniculum vulgare Mill: a review of its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, contemporary application, and toxicology.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:842674. doi: 10.1155/2014/842674. Epub 2014 Aug 3. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25162032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening & analysis of anionic peptides from Foeniculum vulgare Mill by mass spectroscopy.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019 May;26(4):660-664. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31048989 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of a fennel seed extract on the STAT signaling and intestinal barrier function.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 8;17(7):e0271045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271045. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35802574 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: State of the Art, In Silico Prediction and Perspectives in the Omics Era.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020 Sep 2;14:1177932220952739. doi: 10.1177/1177932220952739. eCollection 2020. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020. PMID: 32952397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Based Drugs and Drug Delivery Systems.Molecules. 2017 Dec 8;22(12):2185. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122185. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29292757 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Updated Review on Plant Peptides and Their Applications in Human Health.Int J Pept Res Ther. 2022;28(5):135. doi: 10.1007/s10989-022-10437-7. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35911180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

