Icteric human samples: Icterus index and method of estimating an interference-free value for 16 biochemical analyses
- PMID: 28397988
- PMCID: PMC6816870
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22229
Icteric human samples: Icterus index and method of estimating an interference-free value for 16 biochemical analyses
Abstract
Background: Hemolysis, Icterus, and Lipemia constituting the HIL index, are the most common causes of interference with accurate measurement in biochemistry. This study focuses on bilirubin interference, aiming to identify the analyses impacted and proposing a way to predict nominal interference-free analyte concentrations, based on both analyte level and Icterus Index (Iict ).
Methods: Sixteen common analytes were studied: alanine aminotransferase (ALT), albumin (ALB), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), amylase (AMY), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total cholesterol (CHOLT), creatinine (CREA, enzymatic method), fructosamine (FRUC), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), HDL cholesterol (HDLc), total iron (Iron), lipase (LIP), inorganic phosphorus (Phos), total protein (PROT), triglycerides (TG), and uric acid (UA). Both the traditional 10% change in concentrations from baseline and the Total Change Level (TCL) were taken as acceptance limits. Nineteen pools of sera covering a wide range of values were tested on the Cobas® 6000 (Roche Diagnostics). Iict ranged from 0 to 60.
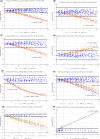
Results: Eight analytes increased (FRUC and Phos) or decreased (CHOLT, CREA, HDLc, PROT, TG, and UA) significantly when Iict increased. FRUC, HDLc, PROT, and UA showed a linear relationship when Iict increased. A non-linear relationship was found for TG, CREA, and for CHOLT; this also depended on analyte levels. Others were not impacted, even at high Iict .
Conclusions: A method of estimating an interference-free value for FRUC, HDLc, PROT, Phos, UA, TG, and CREA, and for CHOLT in cases of cholestasis, is proposed. Iict levels are identified based on analytical performance goals, and equations to recalculate interference-free values are also proposed.
Keywords: bilirubin; biochemistry; correction; icterus index; interference.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Monneret D, Mestari F, Atlan G, et al. Hemolysis indexes for biochemical tests and immunoassays on Roche analyzers: determination of allowable interference limits according to different calculation methods. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015;75:162‐169. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Vargas G, Nordstrom C, Tam E, Buffone GJ, Devaraj S. Effect of interference from hemolysis, icterus and lipemia on routine pediatric clinical chemistry assays. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;438:241‐245. - PubMed
-
- Salvagno GL, Lippi G, Gelati M, Guidi GC. Hemolysis, lipaemia and icterus in specimens for arterial blood gas analysis. Clin Biochem. 2012;45:372‐373. - PubMed
-
- Ji JZ, Meng QH. Evaluation of the interference of hemoglobin, bilirubin, and lipids on Roche Cobas 6000 assays. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412:1550‐1553. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

