Lung hypoplasia in newborn rabbits with a diaphragmatic hernia affects pulmonary ventilation but not perfusion
- PMID: 28399114
- PMCID: PMC5605670
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2017.91
Lung hypoplasia in newborn rabbits with a diaphragmatic hernia affects pulmonary ventilation but not perfusion
Abstract
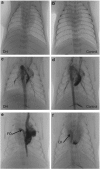
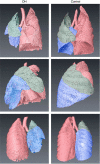
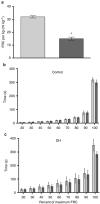
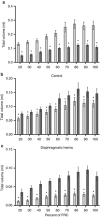
BackgroundA congenital diaphragmatic hernia (DH) can result in severe lung hypoplasia that increases the risk of morbidity and mortality after birth; however, little is known about the cardiorespiratory transition at birth.MethodsUsing phase-contrast X-ray imaging and angiography, we examined the cardiorespiratory transition at birth in rabbit kittens with DHs. Surgery was performed on pregnant New Zealand white rabbits (n=18) at 25 days' gestation to induce a left-sided DH. Kittens were delivered at 30 days' gestation, intubated, and ventilated to achieve a tidal volume (Vt) of 8 ml/kg in control and 4 ml/kg in DH kittens while they were imaged.ResultsFunctional residual capacity (FRC) recruitment and Vt in the hypoplastic left lung were markedly reduced, resulting in a disproportionate distribution of FRC into the right lung. Following lung aeration, relative pulmonary blood flow (PBF) increased equally in both lungs, and the increase in pulmonary venous return was similar in both control and DH kittens.ConclusionThese findings indicate that nonuniform lung hypoplasia caused by DH alters the distribution of ventilation away from hypoplastic and into normally grown lung regions. During transition, the increase in PBF and pulmonary venous return, which is vital for maintaining cardiac output, is not affected by lung hypoplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
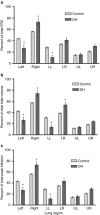
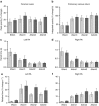
Similar articles
-
Sustained inflation improves initial lung aeration in newborn rabbits with a diaphragmatic hernia.Pediatr Res. 2024 Feb;95(3):660-667. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02874-x. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37952056
-
Antenatal sildenafil treatment improves neonatal pulmonary hemodynamics and gas exchange in lambs with diaphragmatic hernia.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;54(4):506-516. doi: 10.1002/uog.20415. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 31364206
-
Experimental fetal tracheal ligation reverses the structural and physiological effects of pulmonary hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia.J Pediatr Surg. 1994 Feb;29(2):248-56; discussion 256-7. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(94)90328-x. J Pediatr Surg. 1994. PMID: 8176601
-
Advances in prenatal diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014 Dec;19(6):331-7. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Oct 11. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014. PMID: 25306469 Review.
-
Imaging lung aeration and lung liquid clearance at birth using phase contrast X-ray imaging.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009 Jan;36(1):117-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05109.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19205087 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustained inflation improves initial lung aeration in newborn rabbits with a diaphragmatic hernia.Pediatr Res. 2024 Feb;95(3):660-667. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02874-x. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 37952056
-
Intact cord resuscitation in newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: insights from a lamb model.Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 6;11:1236556. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1236556. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37744447 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Gaps in the Fetal to Neonatal Transition of Infants With a Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia.Front Pediatr. 2021 Dec 14;9:784810. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.784810. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34970518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal stabilisation of infants born with congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a review of current concepts.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020 Jul;105(4):449-454. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2019-318606. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020. PMID: 32170029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reiss I, Schaible T, van den Hout L et al, Standardized postnatal management of infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia in Europe: the CDH EURO Consortium consensus. Neonatology 2010;98:354–64. - PubMed
-
- Logan JW, Rice HE, Goldberg RN, Cotten CM. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a systematic review and summary of best-evidence practice strategies. J Perinatol 2007;27:535–49. - PubMed
-
- Snoek KG, Reiss IK, Greenough A et al, Standardized postnatal management of infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia in Europe: the CDH EURO Consortium Consensus - 2015 update. Neonatology 2016;110:66–74. - PubMed
-
- Kotecha S, Barbato A, Bush A et al, Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Eur Respir J 2012;39:820–9. - PubMed
-
- Logan JW, Cotten CM, Goldberg RN, Clark RH. Mechanical ventilation strategies in the management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Pediatr Surg 2007;16:115–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

