Levels of hepatic Th17 cells and regulatory T cells upregulated by hepatic stellate cells in advanced HBV-related liver fibrosis
- PMID: 28399886
- PMCID: PMC5387242
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1167-y
Levels of hepatic Th17 cells and regulatory T cells upregulated by hepatic stellate cells in advanced HBV-related liver fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Liver fibrosis which mainly occurs upon chronic hepatitis virus infection potentially leads to portal hypertension, hepatic failure and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the immune status of Th17 and Treg cells in liver fibrosis is controversial and the exact mechanisms remain largely elusive.
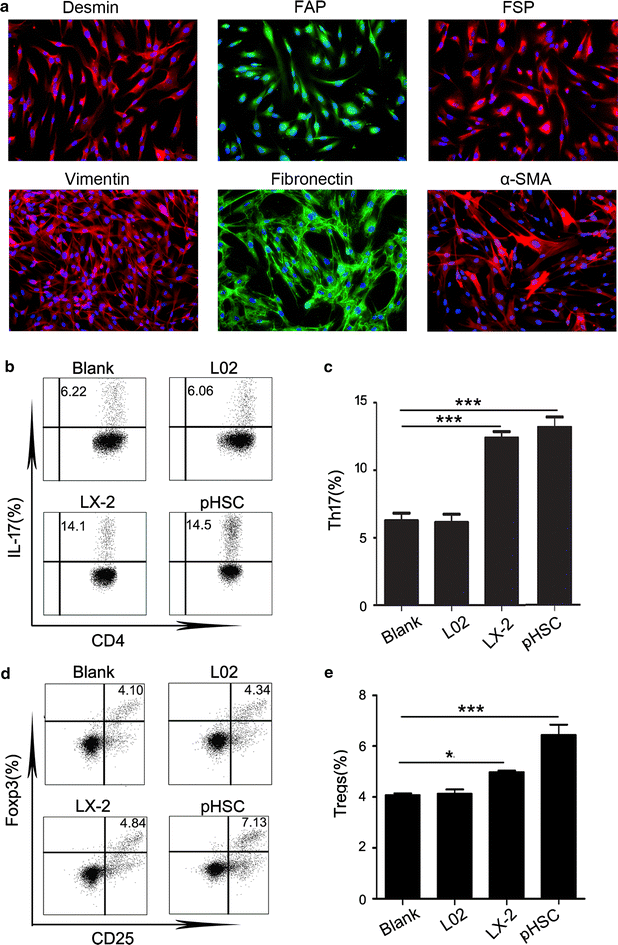
Methods: Liver tissues and peripheral blood were obtained simultaneously from 32 hepatitis B virus infected patients undergoing surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma at the medical center of Sun Yat-sen University. Liver tissues at least 3 cm away from the tumor site were used for the analyses. Levels of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells were detected by flow cytometry analysis and immunohistochemistry. In vitro experiment, we adopted magnetic cell sorting to investigate how hepatic stellate cells regulate the levels of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells.
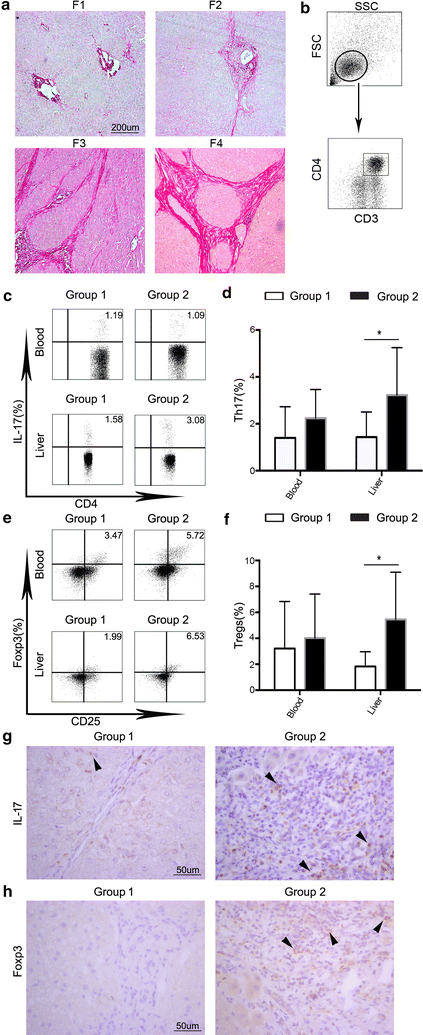
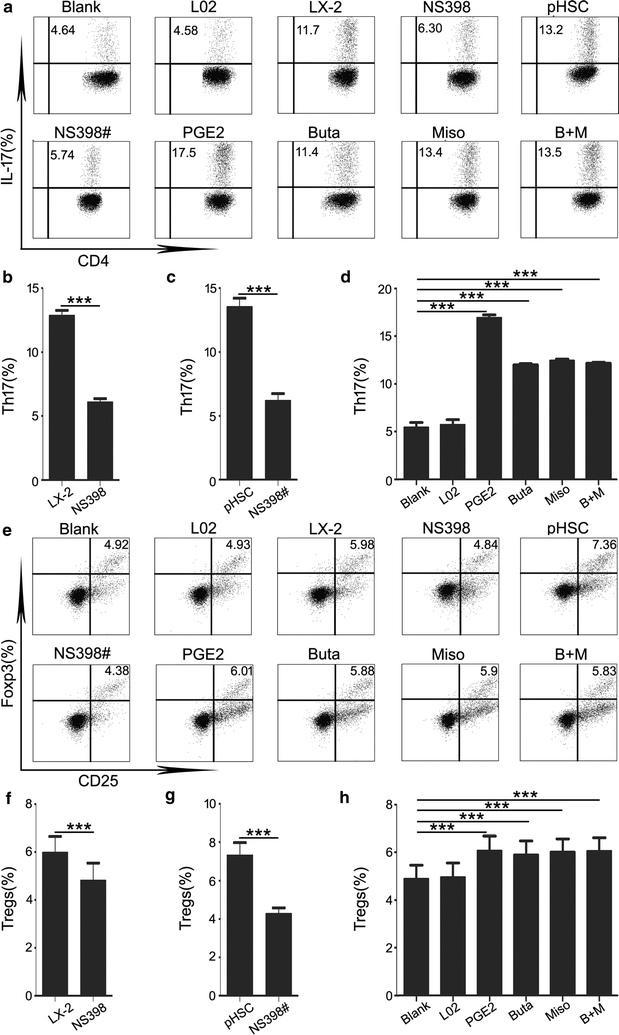
Results: We found that hepatic Th17 cells and regulatory T cells were increased in patients with advanced stage HBV-related liver fibrosis. Hepatic stellate cells upregulated the levels of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells via PGE2/EP2 and EP4 pathway.
Conclusions: We found that the increased levels of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells were upregulated by hepatic stellate cells. These results may provide insight into the role of hepatic stellate cells and Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in the persistence of fibrosis and into the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma following cirrhosis.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cells; Liver fibrosis, HCC; Regulatory T cells; Th17 cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated hepatic stellate cells directly induce pathogenic Th17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Oct 1;359(1):129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28780305
-
Significance of the balance between regulatory T (Treg) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells during hepatitis B virus related liver fibrosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039307. Epub 2012 Jun 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22745730 Free PMC article.
-
Ratios of regulatory T cells/T-helper 17 cells and transforming growth factor-β1/interleukin-17 to be associated with the development of hepatitis B virus-associated liver cirrhosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 May;29(5):1065-72. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12459. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24236690
-
Restoring homeostasis of CD4⁺ T cells in hepatitis-B-virus-related liver fibrosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 14;21(38):10721-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10721. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26478664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual effect of T helper cell 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cell (Treg) in liver pathological process: From occurrence to end stage of disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Apr;69:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Jan 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30669025 Review.
Cited by
-
[Effects of hepatitis B virus on Th17, Treg and Th17/Treg ratio in different alanine aminetransferase stages].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Apr 18;54(2):272-277. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.012. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35435191 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Pathogenetic Mechanisms of T Cell Dysfunction in Chronic HBV Infection and Related Therapeutic Approaches.Front Immunol. 2020 May 12;11:849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00849. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32477347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of class I histone deacetylases attenuate thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice by suppressing hepatic type 2 inflammation.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;176(19):3775-3790. doi: 10.1111/bph.14768. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31236923 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Induce Infiltration and Formation of CD163+ Macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 Pathway.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 5;8:627927. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.627927. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33614685 Free PMC article.
-
The role of immune regulation in HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinogenesis.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 14;16:1506526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1506526. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40160817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

