Suppression of Lymphocyte Functions by Plasma Exosomes Correlates with Disease Activity in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- PMID: 28400428
- PMCID: PMC5559308
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2819
Suppression of Lymphocyte Functions by Plasma Exosomes Correlates with Disease Activity in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
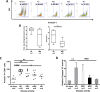
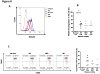
Purpose: Head and neck cancers (HNCs) often induce profound immunosuppression, which contributes to disease progression and interferes with immune-based therapies. Body fluids of patients with HNC are enriched in exosomes potentially engaged in negative regulation of antitumor immune responses. The presence and content of exosomes derived from plasma of patients with HNC are evaluated for the ability to induce immune dysfunction and influence disease activity.Experimental Design: Exosomes were isolated by size-exclusion chromatography from plasma of 38 patients with HNC and 14 healthy donors. Morphology, size, numbers, and protein and molecular contents of the recovered exosomes were determined. Coculture assays were performed to measure exosome-mediated effects on functions of normal human lymphocyte subsets and natural killer (NK) cells. The results were correlated with disease stage and activity.Results: The presence, quantity, and molecular content of isolated, plasma-derived exosomes discriminated patients with HNC with active disease (AD) from those with no evident disease (NED) after oncologic therapies. Exosomes of patients with AD were significantly more effective than exosomes of patients with NED in inducing apoptosis of CD8+ T cells, suppression of CD4+ T-cell proliferation, and upregulation of regulatory T-cell (Treg) suppressor functions (all at P < 0.05). Exosomes of patients with AD also downregulated NKG2D expression levels in NK cells.Conclusions: Exosomes in plasma of patients with HNC carry immunosuppressive molecules and interfere with functions of immune cells. Exosome-induced immune suppression correlates with disease activity in HNC, suggesting that plasma exosomes could be useful as biomarkers of HNC progression. Clin Cancer Res; 23(16); 4843-54. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Figures
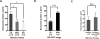
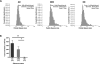




Similar articles
-
Clinical Significance of PD-L1+ Exosomes in Plasma of Head and Neck Cancer Patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 15;24(4):896-905. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2664. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29233903 Free PMC article.
-
Immune modulation of T-cell and NK (natural killer) cell activities by TEXs (tumour-derived exosomes).Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Feb 1;41(1):245-51. doi: 10.1042/BST20120265. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23356291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Separation of plasma-derived exosomes into CD3(+) and CD3(-) fractions allows for association of immune cell and tumour cell markers with disease activity in HNSCC patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Jun;192(3):271-283. doi: 10.1111/cei.13113. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29431869 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages play an essential role in antigen-specific immune suppression mediated by T CD8⁺ cell-derived exosomes.Immunology. 2015 Sep;146(1):23-32. doi: 10.1111/imm.12466. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25808106 Free PMC article.
-
Head and Neck Carcinoma Immunotherapy: Facts and Hopes.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 1;24(1):6-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1261. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 28751445 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of MM cell-derived exosomes in T lymphocytes immune responses.Oncol Lett. 2020 Oct;20(4):31. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11892. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32774504 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and analysis of tumor‑derived extracellular vesicles from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma plasma by galectin‑based glycan recognition particles.Int J Oncol. 2022 Nov;61(5):133. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5423. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36129151 Free PMC article.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in circulating tumor cell-mediated distant metastasis.Mol Cancer. 2023 Nov 30;22(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01909-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38037077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal CD73 from serum of patients with melanoma suppresses lymphocyte functions and is associated with therapy resistance to anti-PD-1 agents.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Mar;10(3):e004043. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004043. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35273100 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-related LncRNAs are correlated with immunity and predict prognosis in HNSC independent of TMB.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 1;14:1028044. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1028044. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36816017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferris RL, Whiteside TL, Ferrone S. Immune escape associated with functional defects in antigen-processing machinery in head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3890–5. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann C, Strauss L, Zeidler R, Lang S, Whiteside TL. Expansion of human T regulatory type 1 cells in the microenvironment of cyclooxygenase 2 overexpressing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8865–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

