Convergence of DNA methylation and phosphorothioation epigenetics in bacterial genomes
- PMID: 28400512
- PMCID: PMC5410841
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1702450114
Convergence of DNA methylation and phosphorothioation epigenetics in bacterial genomes
Abstract
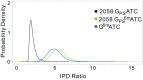
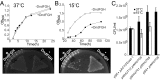
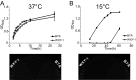
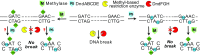
Explosive growth in the study of microbial epigenetics has revealed a diversity of chemical structures and biological functions of DNA modifications in restriction-modification (R-M) and basic genetic processes. Here, we describe the discovery of shared consensus sequences for two seemingly unrelated DNA modification systems, 6mA methylation and phosphorothioation (PT), in which sulfur replaces a nonbridging oxygen in the DNA backbone. Mass spectrometric analysis of DNA from Escherichia coli B7A and Salmonella enterica serovar Cerro 87, strains possessing PT-based R-M genes, revealed d(GPS6mA) dinucleotides in the GPS6mAAC consensus representing ∼5% of the 1,100 to 1,300 PT-modified d(GPSA) motifs per genome, with 6mA arising from a yet-to-be-identified methyltransferase. To further explore PT and 6mA in another consensus sequence, GPS6mATC, we engineered a strain of E. coli HST04 to express Dnd genes from Hahella chejuensis KCTC2396 (PT in GPSATC) and Dam methyltransferase from E. coli DH10B (6mA in G6mATC). Based on this model, in vitro studies revealed reduced Dam activity in GPSATC-containing oligonucleotides whereas single-molecule real-time sequencing of HST04 DNA revealed 6mA in all 2,058 GPSATC sites (5% of 37,698 total GATC sites). This model system also revealed temperature-sensitive restriction by DndFGH in KCTC2396 and B7A, which was exploited to discover that 6mA can substitute for PT to confer resistance to restriction by the DndFGH system. These results point to complex but unappreciated interactions between DNA modification systems and raise the possibility of coevolution of interacting systems to facilitate the function of each.
Keywords: DNA methylation; DNA phosphorothioation; bioanalytical chemistry; epigenetics; restriction–modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epigenetic competition reveals density-dependent regulation and target site plasticity of phosphorothioate epigenetics in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 23;117(25):14322-14330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2002933117. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32518115 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence, evolution, and functions of DNA phosphorothioate epigenetics in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 27;115(13):E2988-E2996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721916115. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29531068 Free PMC article.
-
A DNA phosphorothioation-based Dnd defense system provides resistance against various phages and is compatible with the Ssp defense system.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0093323. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00933-23. Epub 2023 Jun 1. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37260233 Free PMC article.
-
DNA phosphorothioate modification-a new multi-functional epigenetic system in bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2019 Mar 1;43(2):109-122. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuy036. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30289455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Helicobacter pylori Methylome: Roles in Gene Regulation and Virulence.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:105-127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28124151 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial genetics and molecular pathogenesis in the age of high throughput DNA sequencing.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020 Apr;54:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32044689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PacBio sequencing of human fecal samples uncovers the DNA methylation landscape of 22 673 gut phages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Dec 11;51(22):12140-12149. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad977. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37904586 Free PMC article.
-
SspABCD-SspE is a phosphorothioation-sensing bacterial defence system with broad anti-phage activities.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Jul;5(7):917-928. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0700-6. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32251370
-
Epigenetic competition reveals density-dependent regulation and target site plasticity of phosphorothioate epigenetics in bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 23;117(25):14322-14330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2002933117. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32518115 Free PMC article.
-
Signature Arsenic Detoxification Pathways in Halomonas sp. Strain GFAJ-1.mBio. 2018 May 1;9(3):e00515-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00515-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29717010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meselson M, Yuan R, Heywood J. Restriction and modification of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:447–466. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal RM, Cheng X. Restriction-modification systems. In: Streips UN, Yasbin RE, editors. Modern Microbial Genetics. 2nd Ed. John Wiley & Sons; New York: 2002. pp. 177–225.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

