The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer
- PMID: 28400788
- PMCID: PMC5368188
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00031
The LIN28/let-7 Pathway in Cancer
Abstract
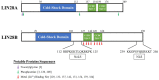
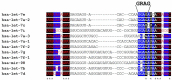
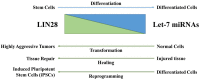
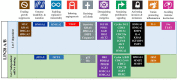
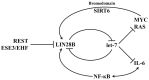
Among all tumor suppressor microRNAs, reduced let-7 expression occurs most frequently in cancer and typically correlates with poor prognosis. Activation of either LIN28A or LIN28B, two highly related RNA binding proteins (RBPs) and proto-oncogenes, is responsible for the global post-transcriptional downregulation of the let-7 microRNA family observed in many cancers. Specifically, LIN28A binds the terminal loop of precursor let-7 and recruits the Terminal Uridylyl Transferase (TUTase) ZCCHC11 that polyuridylates pre-let-7, thereby blocking microRNA biogenesis and tumor suppressor function. For LIN28B, the precise mechanism responsible for let-7 inhibition remains controversial. Functionally, the decrease in let-7 microRNAs leads to overexpression of their oncogenic targets such as MYC, RAS, HMGA2, BLIMP1, among others. Furthermore, mouse models demonstrate that ectopic LIN28 expression is sufficient to drive and/or accelerate tumorigenesis via a let-7 dependent mechanism. In this review, the LIN28/let-7 pathway is discussed, emphasizing its role in tumorigenesis, cancer stem cell biology, metabolomics, metastasis, and resistance to ionizing radiation and several chemotherapies. Also, emerging evidence will be presented suggesting that molecular targeting of this pathway may provide therapeutic benefit in cancer.
Keywords: Lin28; cancer stem cells; let-7; microRNAs; proto-oncogene proteins.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

