Suprascapular Nerve Pathology: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 28400882
- PMCID: PMC5366386
- DOI: 10.2174/1874325001711010140
Suprascapular Nerve Pathology: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
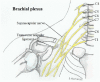
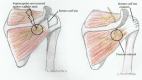
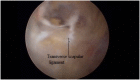
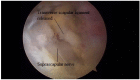
Background: Suprascapular nerve pathology is a rare diagnosis that is increasingly gaining popularity among the conditions that cause shoulder pain and dysfunction. The suprascapular nerve passes through several osseoligamentous structures and can be compressed in several locations.
Methods: A thorough literature search was performed using online available databases in order to carefully define the pathophysiology and to guide diagnosis and treatment.
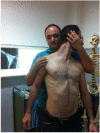
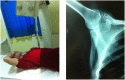
Results: Suprascapular neuropathy diagnosis is based on a careful history and a thorough clinical and radiological examination. Although the incidence and prevalence of the condition remain unknown, it is highly diagnosed in specific groups (overhead athletes, patients with a massive rotator cuff tear) probably due to higher interest. The location and the etiology of the compression are those that define the treatment modality.
Conclusion: Suprascapular neuropathy diagnosis is based on a careful history and a thorough clinical and radiological examination. The purpose of this article is to describe the anatomy of the suprascapular nerve, to define the pathophysiology of suprascapular neuropathy and to present methodically the current diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Keywords: Ligament; Nerve; Neuropathy; Notch; Release; Repair; Review; Rotator cuff; Suprascapular.
Figures





References
-
- Schilf E. Unilateral paralysis of the suprascapular nerve. Nervenarzt. 1952;23(8):306–307. - PubMed
-
- Kopell H.P., Thompson W.A. Pain and the frozen shoulder. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1959;109(1):92–96. - PubMed
-
- Ferretti A., Cerullo G., Russo G. Suprascapular neuropathy in volleyball players. J. Bone Jt. Surg. - Ser. A. 1987;69(2):260–263. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
