Molecular Hydrogen Effectively Heals Alkali-Injured Cornea via Suppression of Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 28400915
- PMCID: PMC5376456
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8906027
Molecular Hydrogen Effectively Heals Alkali-Injured Cornea via Suppression of Oxidative Stress
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Molecular Hydrogen Effectively Heals Alkali-Injured Cornea via Suppression of Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 9;2022:9846572. doi: 10.1155/2022/9846572. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35585887 Free PMC article.
Abstract
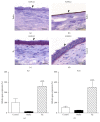
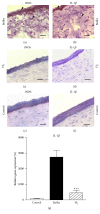
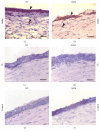
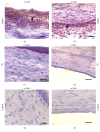
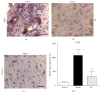
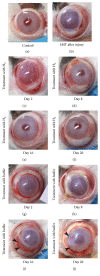
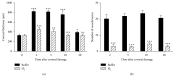
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of molecular hydrogen (H2) on the healing of alkali-injured cornea. The effects of the solution of H2 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or PBS alone topically applied on the alkali-injured rabbit cornea with 0.25 M NaOH were investigated using immunohistochemical and biochemical methods. Central corneal thickness taken as an index of corneal hydration was measured with an ultrasonic pachymeter. Results show that irrigation of the damaged eyes with H2 solution immediately after the injury and then within next five days renewed corneal transparency lost after the injury and reduced corneal hydration increased after the injury to physiological levels within ten days after the injury. In contrast, in injured corneas treated with PBS, the transparency of damaged corneas remained lost and corneal hydration elevated. Later results-on day 20 after the injury-showed that in alkali-injured corneas treated with H2 solution the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, peroxynitrite, detected by nitrotyrosine residues (NT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) expressions were very low or absent compared to PBS treated injured corneas, where NT and MDA expressions were present. In conclusion, H2 solution favorably influenced corneal healing after alkali injury via suppression of oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of alkali-induced oxidative injury in the cornea by mesenchymal stem cells growing on nanofiber scaffolds and transferred onto the damaged corneal surface.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Nov;116:312-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 24145108
-
Treatment of alkali-injured cornea by cyclosporine A-loaded electrospun nanofibers - An alternative mode of therapy.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jun;147:128-137. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 13. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27181227
-
An Immunohistochemical Study of the Increase in Antioxidant Capacity of Corneal Epithelial Cells by Molecular Hydrogen, Leading to the Suppression of Alkali-Induced Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 21;2020:7435260. doi: 10.1155/2020/7435260. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 9;2022:9831406. doi: 10.1155/2022/9831406. PMID: 32655773 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Therapeutic effect of molecular hydrogen in corneal UVB-induced oxidative stress and corneal photodamage.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 21;7(1):18017. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18334-6. Sci Rep. 2017. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 23;11(1):9257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89085-8. PMID: 29269749 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The role of oxidative stress in corneal diseases and injuries.Histol Histopathol. 2015 Aug;30(8):893-900. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-611. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Histol Histopathol. 2015. PMID: 25803192 Review.
Cited by
-
The Healing of Oxidative Injuries with Trehalose in UVB-Irradiated Rabbit Corneas.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Sep 19;2019:1857086. doi: 10.1155/2019/1857086. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Dec 19;2020:4128985. doi: 10.1155/2020/4128985. PMID: 31641422 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The role of hydrogen in Alzheimer's disease.Med Gas Res. 2019 Jan 9;8(4):176-180. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.248270. eCollection 2018 Oct-Dec. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 30713672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retracted: Molecular Hydrogen Effectively Heals Alkali-Injured Cornea via Suppression of Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 9;2022:9846572. doi: 10.1155/2022/9846572. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35585887 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen: A Novel Option in Human Disease Treatment.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 5;2020:8384742. doi: 10.1155/2020/8384742. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32963703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Hydrogen Attenuated N-methyl-N-Nitrosourea Induced Corneal Endothelial Injury by Upregulating Anti-Apoptotic Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34196654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cejkova J., Stipek S., Crkovska J., Ardan T. Changes of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in the corneal epithelium after UVB rays. Histochemical and biochemical study. Histology and Histopathology. 2000;15(4):1043–1050. - PubMed
-
- Čejková J., Štípek S., Crkovská J., Ardan T., Midelfart A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-generating oxidases in the normal rabbit cornea and their involvement in the corneal damage evoked by UVB rays. Histology and Histopathology. 2001;16(2):523–533. - PubMed
-
- Čejková J., Štípek S., Crkovská J., et al. UV rays, the prooxidant/antioxidant imbalance in the cornea and oxidative eye damage. Physiological Research. 2004;53(1):1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

