Thymoquinone Attenuates Brain Injury via an Anti-oxidative Pathway in a Status Epilepticus Rat Model
- PMID: 28400978
- PMCID: PMC5384046
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2017-0003
Thymoquinone Attenuates Brain Injury via an Anti-oxidative Pathway in a Status Epilepticus Rat Model
Abstract
Aim: Status epilepticus (SE) results in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which contribute to seizure-induced brain injury. It is well known that oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in status epilepticus (SE). Thymoquinone (TQ) is a bioactive monomer extracted from black cumin (Nigella sativa) seed oil that has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antioxidant activity in various diseases. This study evaluated the protective effects of TQ on brain injury in a lithium-pilocarpine rat model of SE and investigated the underlying mechanism related to antioxidative pathway.
Methods: Electroencephalogram and Racine scale were used to value seizure severity. Passive-avoidance test was used to determine learning and memory function. Moreover, anti-oxidative activity of TQ was observed using Western blot and super oxide dismutase (SOD) activity assay.
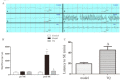
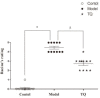
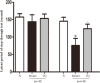
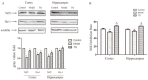
Results: Latency to SE increased in the TQ-pretreated group compared with rats in the model group, while the total power was significantly lower. Seizure severity measured on the Racine scale was significantly lower in the TQ group compared with the model group. Results of behavioral experiments suggest that TQ may also have a protective effect on learning and memory function. Investigation of the protective mechanism of TQ showed that TQ-pretreatment significantly increased the expression of Nrf2, HO-1 proteins and SOD in the hippocampus.
Conclusion: These findings showed that TQ attenuated brain injury induced by SE via an anti-oxidative pathway.
Keywords: Nrf2; brain injury; oxidative stress; status epilepticus; thymoquinone.
Figures
References
-
- Liu J., Wang A., Li L., Huang Y., Xue P., Hao A.. Oxidative stress mediates hippocampal neuron death in rats after lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Seizure. 2010;19:165–172. - PubMed
-
- Smilin Bell Aseervatham G., Sivasudha T., Suganya M., Rameshkumar A., Jeyadevi R.. Trichosanthes tricuspidata modulates oxidative toxicity in brain hippocampus against pilocarpine induced status epilepticus in mice. Neurochem Res. 2013;38:1715–1725. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
