Combining Injectable Plasma Scaffold with Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Repairing Infarct Cavity after Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 28400986
- PMCID: PMC5362179
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2017.0305
Combining Injectable Plasma Scaffold with Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Repairing Infarct Cavity after Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
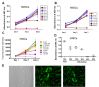
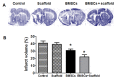
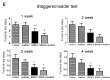
Stroke survivors are typically left with structural brain damage and associated functional impairment in the chronic phase of injury, for which few therapeutic options exist. We reported previously that transplantation of human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived neural stem cells together with Matrigel scaffolding into the brains of rats after focal ischemia reduced infarct volume and improved neurobehavioral performance. Matrigel is a gelatinous protein mixture extracted from mouse sarcoma cells, thus would not be approved for use as a scaffold clinically. In this study, we generated a gel-like scaffold from plasma that was controlled by changing the concentration of CaCl2. In vitro study confirmed that 10-20 mM CaCl2 and 10-40% plasma did not affect the viability and proliferation of human and rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (BMSCs) and neural stem cells (NSCs). We transplanted plasma scaffold in combination of BMSCs into the cystic cavity after focal cerebral ischemia, and found that the atrophy volume was dramatically reduced and motor function was significantly improved in the group transplanted with scaffold/BMSCs compared with the groups treated with vehicle, scaffold or BMSCs only. Our data suggest that plasma-derived scaffold in combination of BMSCs is feasible for tissue engineering approach for the stroke treatment.
Keywords: aging; aging-related diseases; diagnosis; frailty; regulation; senescence.
Figures


References
-
- Brott T, Bogousslavsky J (2000). Treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med, 343:710-722. - PubMed
-
- Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Mao XO, Childs J, Peel A, et al. (2005). Comparison of ischemia-directed migration of neural precursor cells after intrastriatal, intraventricular, or intravenous transplantation in the rat. Neurobiol Dis, 18:366-374. - PubMed
-
- Kondziolka D, Wechsler L, Goldstein S, Meltzer C, Thulborn KR, Gebel J, et al. (2000). Transplantation of cultured human neuronal cells for patients with stroke. Neurology, 55:565-569. - PubMed
-
- Colton CK (1995). Implantable biohybrid artificial organs. Cell Transplant, 4:415-436. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
