High Dose Gamma Radiation Selectively Reduces GABAA-slow Inhibition
- PMID: 28401026
- PMCID: PMC5382012
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1076
High Dose Gamma Radiation Selectively Reduces GABAA-slow Inhibition
Abstract
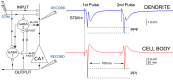
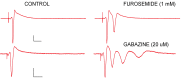
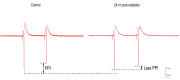
Studies on the effects of gamma radiation on brain tissue have produced markedly differing results, ranging from little effect to major pathology, following irradiation. The present study used control-matched animals to compare effects on a well characterized brain region following gamma irradiation. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to 60 Gy of whole brain gamma radiation and, after 24-hours, 48-hours, and one-week periods, hippocampal brain slices were isolated and measured for anatomical and physiological differences. There were no major changes observed in tissue appearance or evoked synaptic responses at any post-irradiation time point. However, exposure to 60 Gy of irradiation resulted in a small, but statistically significant (14% change; ANOVA p < 0.005; n = 9) reduction in synaptic inhibition seen at 100 ms, indicating a selective depression of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) slow form of inhibition. Population spike (PS) amplitudes also transiently declined by ~ 10% (p < 0.005; n = 9) when comparing the 24-hour group to sham group. Effects on PS amplitude recovered to baseline 48 hour and one week later. There were no obvious negative pathological effects; however, a subtle depression in circuit level inhibition was observed and provides evidence for 'radiomodulation' of brain circuits.
Keywords: brain slice; gaba; gamma; inhibition; pain therapy; radiomodulation; synapse; synaptic inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neuromodulation via Focal Radiation: Radiomodulation Update.Cureus. 2021 Apr 26;13(4):e14700. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14700. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33927960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Volatile anaesthetic enhancement of paired-pulse depression investigated in the rat hippocampus in vitro.J Physiol. 1996 May 1;492 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):823-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021349. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8734993 Free PMC article.
-
Profound disturbances of pre- and postsynaptic GABAB-receptor-mediated processes in region CA1 in a chronic model of temporal lobe epilepsy.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Aug;76(2):1282-96. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.2.1282. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8871236
-
Lindane blocks GABAA-mediated inhibition and modulates pyramidal cell excitability in the rat hippocampal slice.Neurotoxicology. 1995 Summer;16(2):217-28. Neurotoxicology. 1995. PMID: 7566682
-
GABAA-mediated IPSCs in piriform cortex have fast and slow components with different properties and locations on pyramidal cells.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Nov;78(5):2531-45. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.5.2531. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9356403
Cited by
-
Neuromodulation via Focal Radiation: Radiomodulation Update.Cureus. 2021 Apr 26;13(4):e14700. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14700. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33927960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Radioprotective Effect of LBP on Neurogenesis and Cognition after Acute Radiation Exposure.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(3):257-265. doi: 10.2174/0118744710274008231220055033. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 38204264 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of Interneuron Immunoreactivity and Autophagic Activity in Rat Hippocampus after Single High-Dose Whole-Brain Irradiation.Cureus. 2017 Jun 30;9(6):e1414. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1414. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 28861331 Free PMC article.
-
The Neuroprotective Effect of Amitriptyline on Radiation-Induced Impairment of Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Dose Response. 2019 Dec 20;17(4):1559325819895912. doi: 10.1177/1559325819895912. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 31903069 Free PMC article.
-
A newly developed anesthetic based on a unique chemical core.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 30;116(31):15706-15715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1822076116. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31308218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radiobiology of radiosurgery: part I. The normal rat brain model. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Claassen D, et al. http://journals.lww.com/neurosurgery/Abstract/1992/08000/Radiobiology_of.... Neurosurgery. 1992;31:271–279. - PubMed
-
- Response of postmitotic neurons to x-irradiation: Implications for the role of DNA damage in neuronal apoptosis. Gobbel GT, Bellinzona M, Vogt AR, et al. http://www.jneurosci.org/content/18/1/147.short. J Neurosci. 1998;18:147–155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apoptosis is induced in the subependyma of young adult rats by ionizing irradiation. Bellinzona M, Gobbel GT, Shinohara C, et al. Neurosci Lett. 1996;208:163–166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
