Targeting Wolman Disease and Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease: Disease Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Development
- PMID: 28401034
- PMCID: PMC5362971
- DOI: 10.2174/2213988501711010001
Targeting Wolman Disease and Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease: Disease Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Development
Abstract
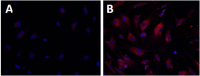
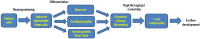
Wolman disease (WD) and cholesteryl ester storage disease (CESD) are lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) caused by a deficiency in lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) due to mutations in the LIPA gene. This enzyme is critical to the proper degradation of cholesterol in the lysosome. LAL function is completely lost in WD while some residual activity remains in CESD. Both are rare diseases with an incidence rate of less than 1/100,000 births for WD and approximate 2.5/100,000 births for CESD. Clinical manifestation of WD includes hepatosplenomegaly, calcified adrenal glands, severe malabsorption and a failure to thrive. As in CESD, histological analysis of WD tissues reveals the accumulation of triglycerides (TGs) and esterified cholesterol (EC) in cellular lysosomes. However, the clinical presentation of CESD is less severe and more variable than WD. This review is to provide an overview of the disease pathophysiology and the current state of therapeutic development for both of WD and CESD. The review will also discuss the application of patient derived iPSCs for further drug discovery.
Keywords: Cell-based disease model; Cholesteryl ester storage disease; High-throughput screening; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Lysosomal storage disease; Wolman disease.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
