Helicobacter pylori Induced Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH Kinase/mTOR Activation Increases Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α to Promote Loss of Cyclin D1 and G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Gastric Cells
- PMID: 28401064
- PMCID: PMC5368181
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00092
Helicobacter pylori Induced Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH Kinase/mTOR Activation Increases Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α to Promote Loss of Cyclin D1 and G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Gastric Cells
Abstract
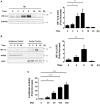
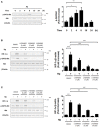
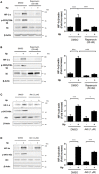
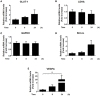
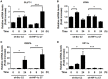
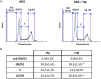
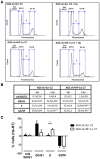
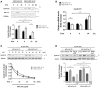
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a human gastric pathogen that has been linked to the development of several gastric pathologies, such as gastritis, peptic ulcer, and gastric cancer. In the gastric epithelium, the bacterium modifies many signaling pathways, resulting in contradictory responses that favor both proliferation and apoptosis. Consistent with such observations, H. pylori activates routes associated with cell cycle progression and cell cycle arrest. H. pylori infection also induces the hypoxia-induced factor HIF-1α, a transcription factor known to promote expression of genes that permit metabolic adaptation to the hypoxic environment in tumors and angiogenesis. Recently, however, also roles for HIF-1α in the repair of damaged DNA and inhibition of gene expression were described. Here, we investigated signaling pathways induced by H. pylori in gastric cells that favor HIF-1α expression and the consequences thereof in infected cells. Our results revealed that H. pylori promoted PI3K/mTOR-dependent HIF-1α induction, HIF-1α translocation to the nucleus, and activity as a transcription factor as evidenced using a reporter assay. Surprisingly, however, transcription of known HIF-1α effector genes evaluated by qPCR analysis, revealed either no change (LDHA and GAPDH), statistically insignificant increases SLC2A1 (GLUT-1) or greatly enhance transcription (VEGFA), but in an HIF-1α-independent manner, as quantified by PCR analysis in cells with shRNA-mediated silencing of HIF-1α. Instead, HIF-1α knockdown facilitated G1/S progression and increased Cyclin D1 protein half-life, via a post-translational pathway. Taken together, these findings link H. pylori-induced PI3K-mTOR activation to HIF-1α induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest by a Cyclin D1-dependent mechanism. Thus, HIF-1α is identified here as a mediator between survival and cell cycle arrest signaling activated by H. pylori infection.
Keywords: Cyclin D1; HIF-1α; Helicobacter pylori; PI3K/mTOR; cell cycle arrest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori induces vascular endothelial growth factor production in gastric epithelial cells through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-dependent pathway.Helicobacter. 2014 Dec;19(6):476-83. doi: 10.1111/hel.12169. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Helicobacter. 2014. PMID: 25231285
-
Sirolimus increases the anti-cancer effect of Huai Er by regulating hypoxia inducible factor-1α-mediated glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 28;28(32):4600-4619. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4600. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36157928 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of KLF5 suppresses hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin in NSCLC cells by regulating HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.J Transl Med. 2018 Jun 14;16(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1543-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29898734 Free PMC article.
-
Is the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway important in gastric cancer?Eur J Cancer. 2005 Dec;41(18):2792-805. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Eur J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16290133 Review.
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jan 26;29(1):71-91. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28822229 Review.
Cited by
-
Garcinol-Attenuated Gastric Ulcer (GU) Experimentally Induced in Rats Via Affecting Inflammation, Cell Proliferation, and DNA Polymerization.Cureus. 2023 Aug 11;15(8):e43317. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43317. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37577271 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jul 15;16(7):3270-3283. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i7.3270. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39072157 Free PMC article.
-
More powerful dysregulation of Helicobacter pylori East Asian-type CagA on intracellular signalings.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Nov 11;24(1):467. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03619-4. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39528935 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori Immune Response in Children Versus Adults.Med Res Arch. 2022 Dec;10(12):3370. doi: 10.18103/mra.v10i12.3370. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Med Res Arch. 2022. PMID: 37936946 Free PMC article.
-
Oral rinses in growth inhibition and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01728-4. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32131741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya A., Chattopadhyay R., Hall E. H., Mebrahtu S. T., Ernst P. B., Crowe S. E. (2010). Mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-mediated Mcl1 regulation in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 299, G1177–G1186. 10.1152/ajpgi.00372.2010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

