CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted gene correction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient iPSCs
- PMID: 28401346
- PMCID: PMC5413600
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-017-0397-3
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted gene correction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient iPSCs
Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a complex neurodegenerative disease with cellular and molecular mechanisms yet to be fully described. Mutations in a number of genes including SOD1 and FUS are associated with familial ALS. Here we report the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from fibroblasts of familial ALS patients bearing SOD1 +/A272C and FUS +/G1566A mutations, respectively. We further generated gene corrected ALS iPSCs using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Genome-wide RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of motor neurons derived from SOD1 +/A272C and corrected iPSCs revealed 899 aberrant transcripts. Our work may shed light on discovery of early biomarkers and pathways dysregulated in ALS, as well as provide a basis for novel therapeutic strategies to treat ALS.
Keywords: ALS; CRISPR/Cas9; gene correction; iPSC disease modeling.
Figures
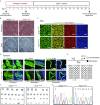


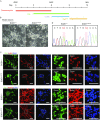
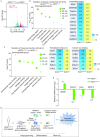
References
-
- Alexianu ME, Ho BK, Mohamed AH, La Bella V, Smith RG, Appel SH (1994) The role of calcium-binding proteins in selective motoneuron vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36:846–858 - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Catania MV, Geurts J, Yankaya B, Troost D (2001) Immunohistochemical localization of group I and II metabotropic glutamate receptors in control and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis human spinal cord: upregulation in reactive astrocytes. Neuroscience 105:509–520 - PubMed
-
- Baechtold H, Kuroda M, Sok J, Ron D, , Lopez BS, Akhmedov AT (1999) Human 75-kDa DNA-pairing protein is identical to the pro-oncoprotein TLS/FUS and is able to promote D-loop formation. J Biol Chem 274:34337–34342 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

