Long-term follow-up of fenestrated endovascular repair for juxtarenal aortic aneurysm
- PMID: 28401533
- PMCID: PMC5485015
- DOI: 10.1002/bjs.10524
Long-term follow-up of fenestrated endovascular repair for juxtarenal aortic aneurysm
Abstract
Background: Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) is increasingly being used for juxtarenal aortic aneurysms. The aim of this study was to review long-term results and assess the importance of changing stent-graft design on outcomes.
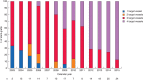
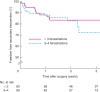
Methods: This was a retrospective review of all patients who underwent FEVAR within a single unit over 12 years (February 2003 to December 2015). Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival, and freedom from target vessel loss, aneurysm expansion, graft-related endoleak and secondary intervention was performed. Comparison between outcomes of less complex grafts (fewer than 3 fenestrations) and more complex grafts (3 or 4 fenestrations) was undertaken.
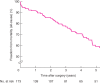
Results: Some 173 patients underwent FEVAR; median age was 76 (i.q.r. 70-79) years and 90·2 per cent were men. Median aneurysm diameter was 63 (59-71) mm and median follow-up was 34 (16-50) months. The adjusted primary technical operative success rate was 95·4 per cent. The in-hospital mortality rate was 5·2 per cent; there was no known aneurysm-related death during follow-up. Median survival was 7·1 (95 per cent c.i. 5·2 to 8·1) years and overall survival was 60·1 per cent (104 of 173). There was a trend towards an increasing number of fenestrations in the graft design over time. In-hospital mortality appeared higher when more complex stent-grafts were used (8 versus 2 per cent for stent-grafts with 3-4 versus fewer than 3 fenestrations; P = 0·059). Graft-related endoleaks were more common following deployment of stent-grafts with three or four fenestrations (12 of 90 versus 6 of 83; P < 0·001).
Conclusion: Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair for juxtarenal aneurysm is associated with few aneurysm-related deaths in the long term. Significant numbers of secondary interventions are required, but the majority of these can be performed using an endovascular approach.
© 2017 The Authors. BJS published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJS Society Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Browne TF, Hartley D, Purchas S, Rosenberg M, Van Schie G, Lawrence‐Brown M. A fenestrated covered suprarenal aortic stent. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 1999; 18: 445–449. - PubMed
-
- Waton S, Johal A, Heikkila K, Cromwell D, Loftus I. National Vascular Registry: 2015 Annual Report. Royal College of Surgeons of England: London, 2015.
-
- British Society for Endovascular Therapy and the Global Collaborators on Advanced Stent‐Graft Techniques for Aneurysm Repair (GLOBALSTAR) Registry . Early results of fenestrated endovascular repair of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms in the United Kingdom. Circulation 2012; 125: 2707–2715. - PubMed
-
- Kristmundsson T, Sonesson B, Dias N, Törnqvist P, Malina M, Resch T. Outcomes of fenestrated endovascular repair of juxtarenal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg 2014; 59: 115–120. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

