Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence by simultaneously targeting pneumolysin and sortase A
- PMID: 28402019
- PMCID: PMC5618700
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13179
Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence by simultaneously targeting pneumolysin and sortase A
Abstract
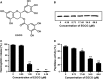
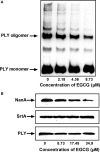
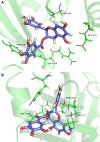
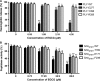
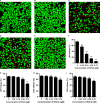
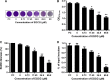
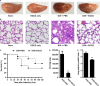
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), the causative agent of several human diseases, possesses numerous virulence factors associated with pneumococcal infection and pathogenesis. Pneumolysin (PLY), an important virulence factor, is a member of the cholesterol-dependent cytolysin family and has cytolytic activity. Sortase A (SrtA), another crucial pneumococcal virulence determinate, contributes greatly to the anchoring of many virulence-associated surface proteins to the cell wall. In this study, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a natural compound with little known antipneumococcal activity, was shown to directly inhibit PLY-mediated haemolysis and cytolysis by blocking the oligomerization of PLY and simultaneously reduce the peptidase activity of SrtA. The biofilm formation, production of neuraminidase A (NanA, the pneumococcal surface protein anchored by SrtA), and bacterial adhesion to human epithelial cells (Hep2) were inhibited effectively when S. pneumoniae D39 was cocultured with EGCG. The results from molecular dynamics simulations and mutational analysis confirmed the interaction of EGCG with PLY and SrtA, and EGCG binds to Glu277, Tyr358, and Arg359 in PLY and Thr169, Lys171, and Phe239 in SrtA. In vivo studies further demonstrated that EGCG protected mice against S. pneumoniae pneumonia. Our results imply that EGCG is an effective inhibitor of both PLY and SrtA and that an antivirulence strategy that directly targets PLY and SrtA using EGCG is a promising therapeutic option for S. pneumoniae pneumonia.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; antivirulence; epigallocatechin gallate; neuraminidases A; pneumolysin; sortase A.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Nel JG, Durandt C, Mitchell TJ, et al Pneumolysin mediates platelet activation in vitro . Lung. 2016; 194: 589–93. - PubMed
-
- Bogaert D, van Belkum A, Sluijter M, et al Colonisation by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in healthy children. Lancet. 2004; 363: 1871–2. - PubMed
-
- Brittan JL, Buckeridge TJ, Finn A, et al Pneumococcal neuraminidase A: an essential upper airway colonization factor for Streptococcus pneumoniae . Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012; 27: 270–83. - PubMed
-
- Feldman C, Munro NC, Jeffery PK, et al Pneumolysin induces the salient histologic features of pneumococcal infection in the rat lung in vivo . Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991; 5: 416–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

